zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs)
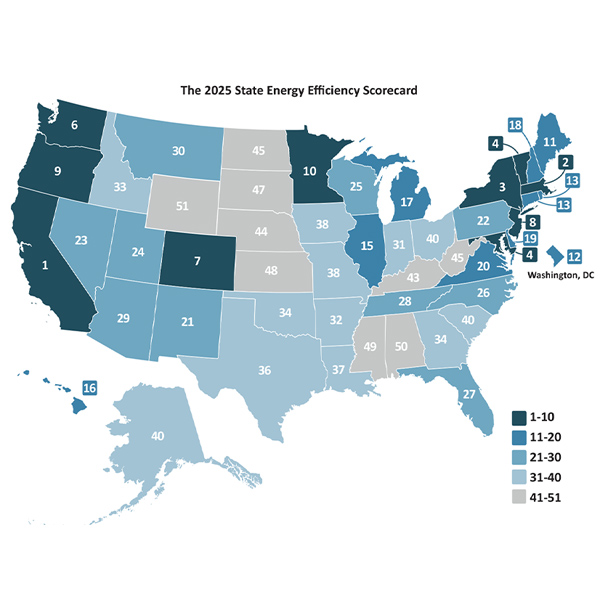
The 16th ACEEE state energy efficiency scorecard put California at the top of the rankings and Wyoming at the bottom.
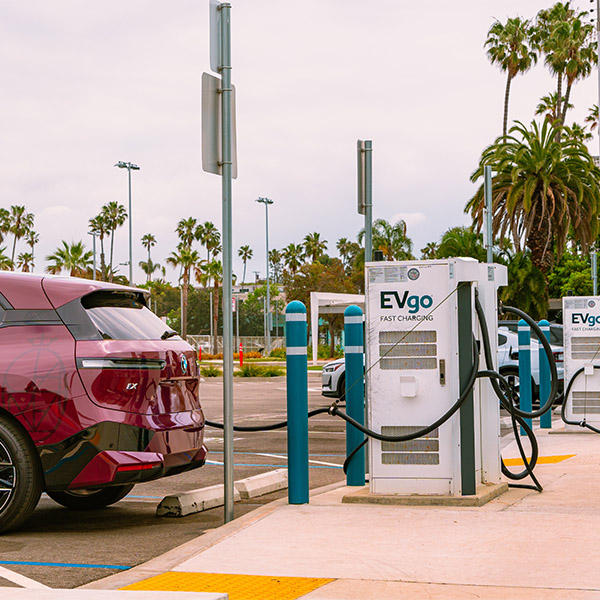
California regulators approved a $95.2 million funding plan for zero-emission vehicle charging infrastructure, with nearly equal amounts going to charging for passenger vehicles and medium- and heavy-duty trucks.
California regulators approved a $35 million package of clean transportation incentives for fiscal year 2024/25, a steep drop in funding that is raising concerns about the fate of programs not funded by the package.
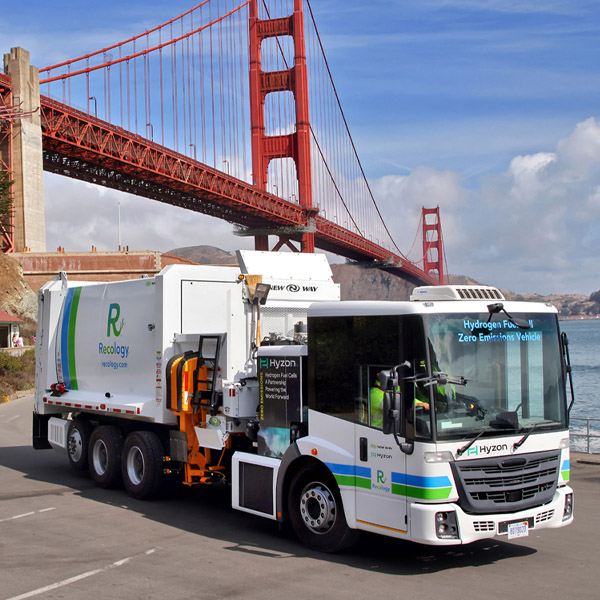
California regulators have approved changes to a zero-emission truck regulation to make compliance easier, keeping their end of a deal with truck manufacturers over the transition to ZEVs.
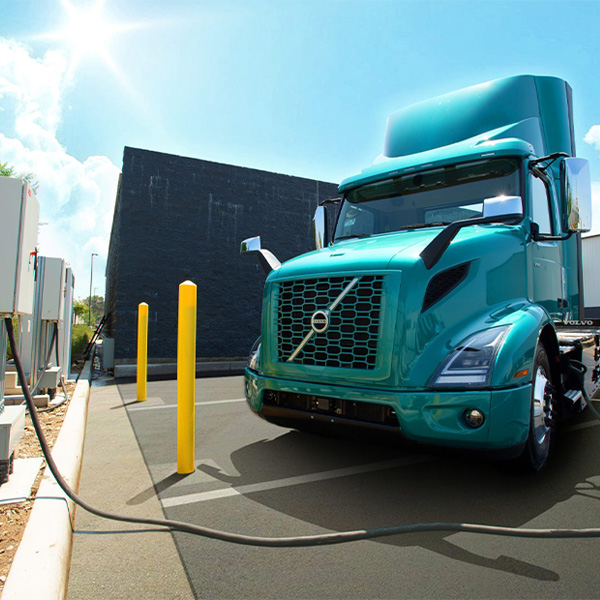
California ZEV infrastructure projects are receiving $150 million in federal funding, including $102 million for a tri-state charging network for medium- and heavy-duty trucks.
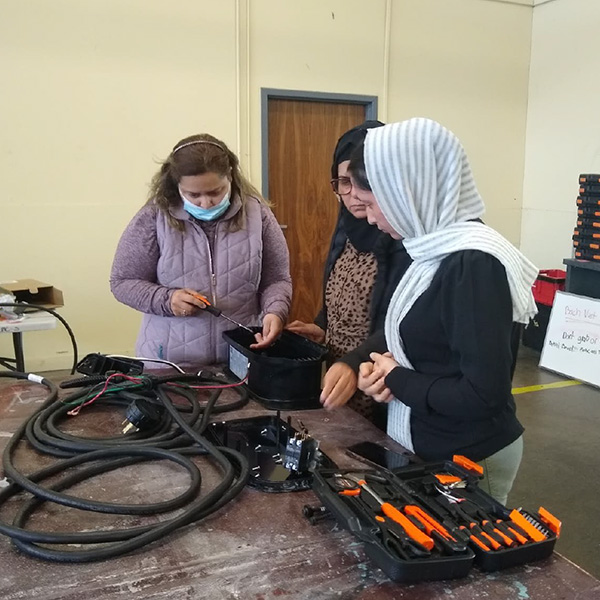
California officials described how their agencies plan to address the shortage of skilled workers needed to support the state’s transition to zero-emission vehicles.
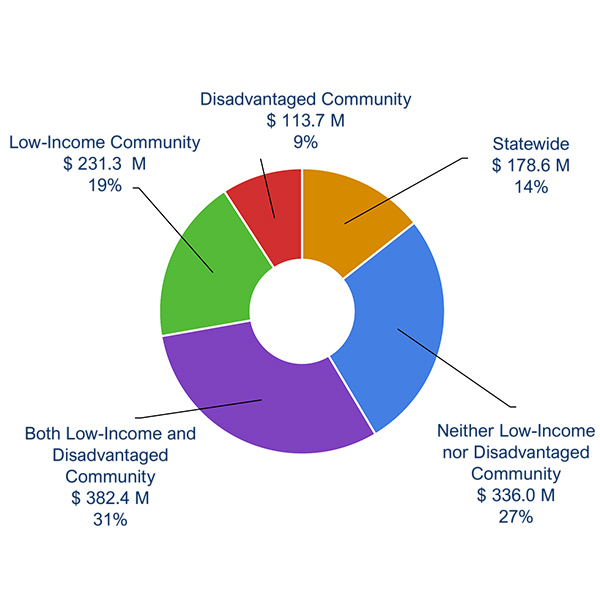
California must find ways to allocate more of its funding for ZEV infrastructure to disadvantaged communities, according to an advisory committee for the Energy Commission's Clean Transportation Program Investment Plan.
An estimated 72 million Americans, often people of color or with low incomes, live near truck routes that expose them to pollution resulting in higher rates of respiratory and cardiovascular illnesses and premature death.
A new report finds that U.S. zero-emission vehicle sales meet industry expectations set upon passage of the IRA but utility-scale clean electricity expansion fall short.
The California Energy Commission approved a plan for spending $1.85 billion over the next four years to expand zero-emission vehicle infrastructure across the state.
Want more? Advanced Search