pay-for-performance
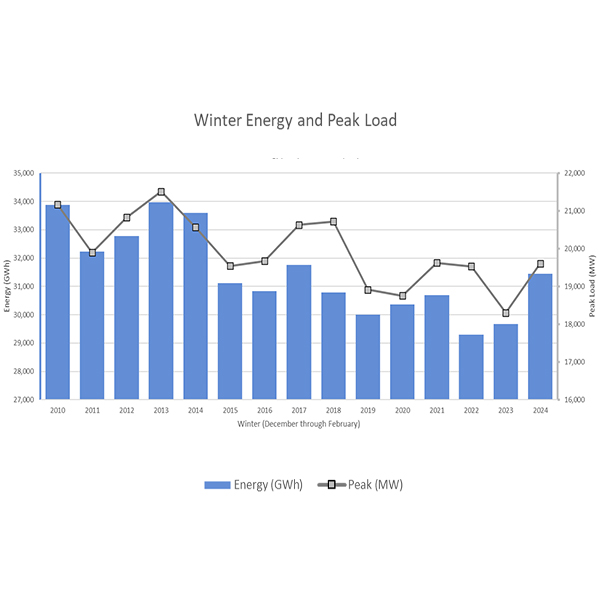
New England energy market revenues increased by roughly 150% in the winter of 2024/25 compared to the prior winter.
FERC accepted ISO-NE’s proposal to increase the collateral requirements for generators participating in its capacity market, rejecting the New England Power Generators Association’s arguments that the changes violate the filed rate doctrine.
The NEPOOL Participants Committee voted to update the Generation Information System to enable the transfer of hourly certificates, opening the door for the sale of hourly renewable energy credits.
Governance structures and market rules at ISO-NE that favor incumbent interests have contributed to pushing the region into costly and carbon-intensive reliability solutions, law professor Joshua Macey told the Consumer Liaison Group.
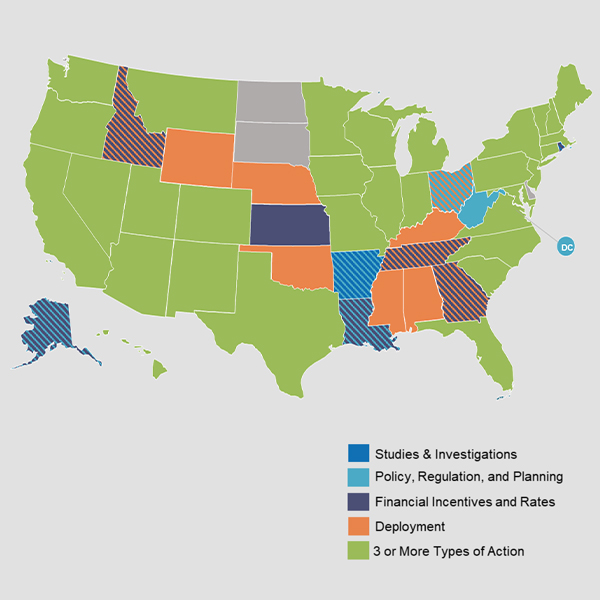
States need to fund, shape and incentivize projects that contribute to their emission-reduction goals, a speaker told New Jersey’s Clean Energy Conference.
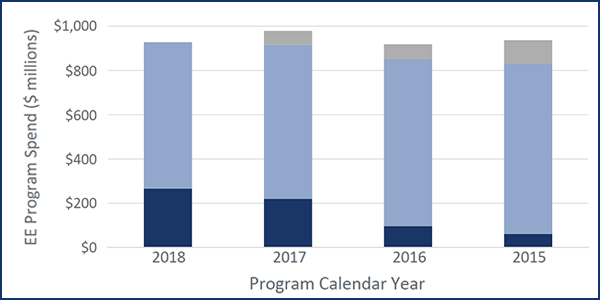
ISO-NE told stakeholders it will file a rule change with FERC to eliminate capacity performance payments from energy efficiency resources.
The NEPOOL Markets Committee devoted the bulk of its meeting to debating changes to inputs and assumptions that will govern FCA 16 in February 2022.
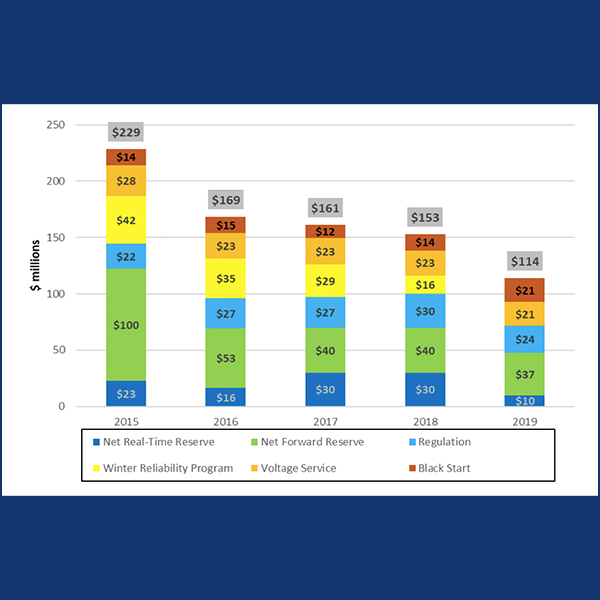
New England’s total wholesale costs of electricity last year fell 19% to $9.8 billion, according to the ISO-NE Market Monitor’s 2019 Annual Markets Report.
The New England Power Pool Markets Committee rejected ISO-NE’s interim proposal for compensating generators for fuel security. But the RTO plans to file the plan with FERC with or without stakeholder endorsement.
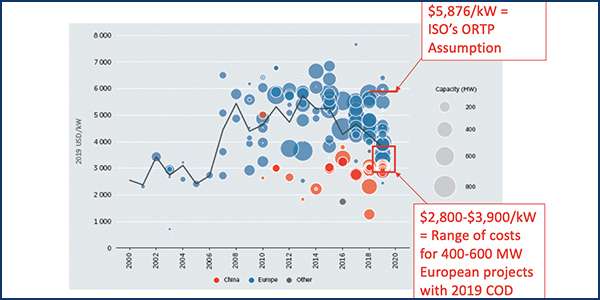
ISO-NE CEO Gordon van Welie said his concerns about New England’s ability to keep the lights on continue to grow despite enacted market rule changes.
Want more? Advanced Search