critical infrastructure protection (CIP)
FERC took the last step in fulfilling its obligation to encourage voluntary investments in cybersecurity by electric utilities, as directed by Congress in 2021.
NERC will consider changes to its reliability standard for physical security in response to the threat of violence against grid assets.
FERC acted to shore up grid cybersecurity defenses by approving a NERC reliability standard that requires utilities to protect low-impact cyber resources.
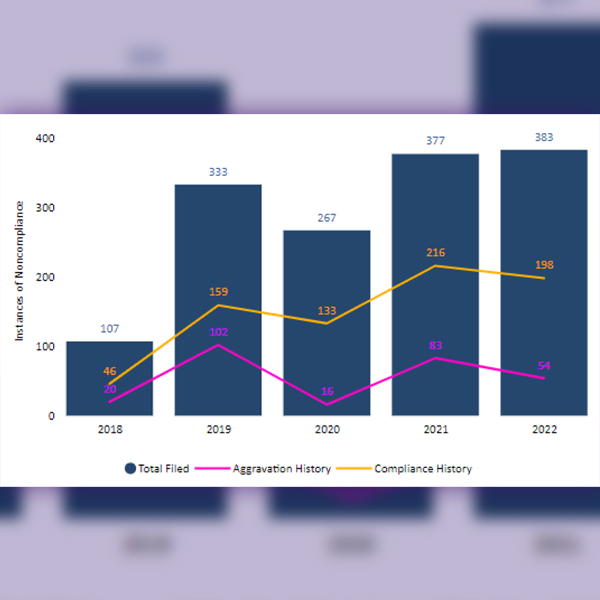
2022 saw “significant progress” for the ERO’s Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement and Organization Registration and Certification programs, a new report says.
PJM and its IMM gave first reads of their proposals exploring whether generators should be permitted to recover upgrade costs for some critical facilities.
The electric industry still is not taking its critical infrastructure protection (CIP) programs as seriously as they should, panelists told ReliabilityFirst.
FERC ordered NERC to require utilities to implement internal network security monitoring on certain cyber systems at bulk power system facilities.
The commission rejected a complaint by cybersecurity activist George Cotter, who last year accused NERC of neglecting the cybersecurity needs of the BPS.
The OC rejected modifications to its issue charge exploring costs for generators deemed critical to maintaining interconnection reliability operating limits.
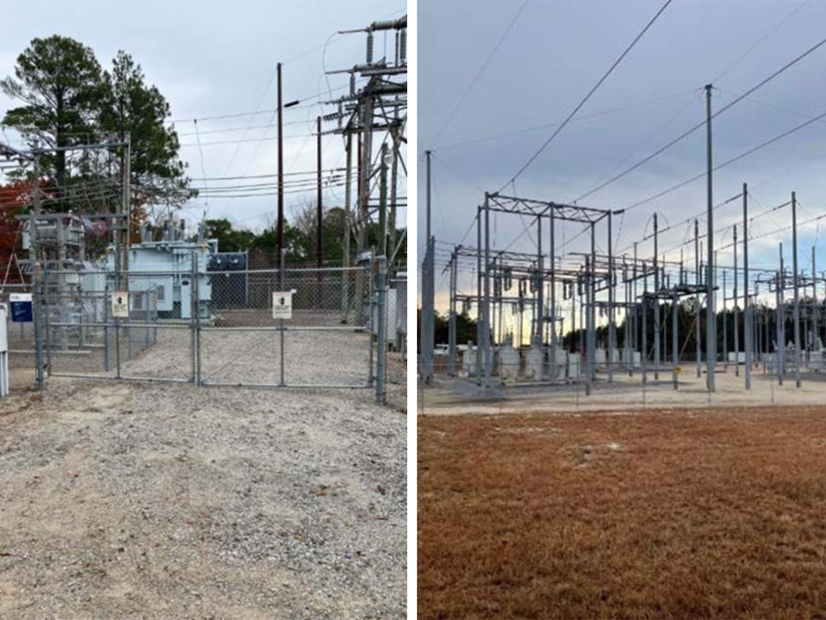
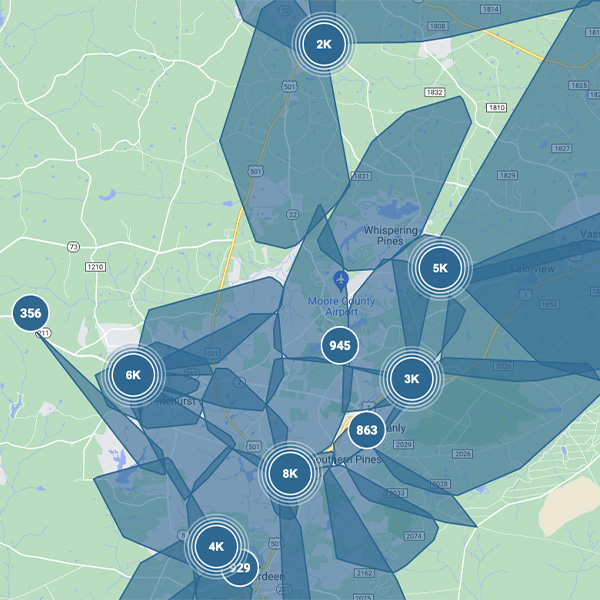
More than 33,000 customers remain without power in Moore County, N.C., following apparent attacks on two of Duke Energy’s substations over the weekend.
Want more? Advanced Search