cost of new entry (CONE)
Potomac Economics’ 2019 State of the Market Report for NYISO adds five recommendations while concluding the ISO’s markets “performed competitively” in 2019.
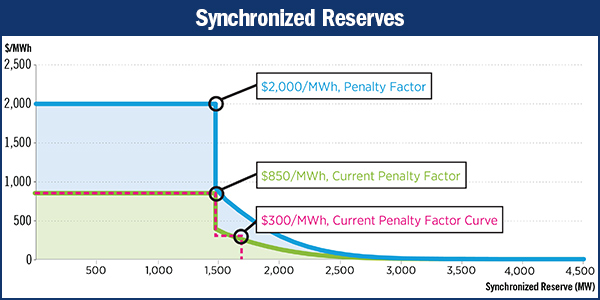
FERC approved PJM’s proposed energy price formation revisions, agreeing with the RTO that its reserve market was not functioning as intended.
ISO-NE’s winter wholesale market costs totaled $1.8 billion, a 32% decrease from the previous winter because of lower energy and capacity costs.
PJM shared its initial response to FERC’s April 16 rehearing orders on the MOPR, which required the RTO to make an additional compliance filing by June 1.
MISO’s capacity auction marked the RTO’s first clearing price set by its cost of new entry, as prices in the Lower Peninsula rocketed to almost $260/MW-day.
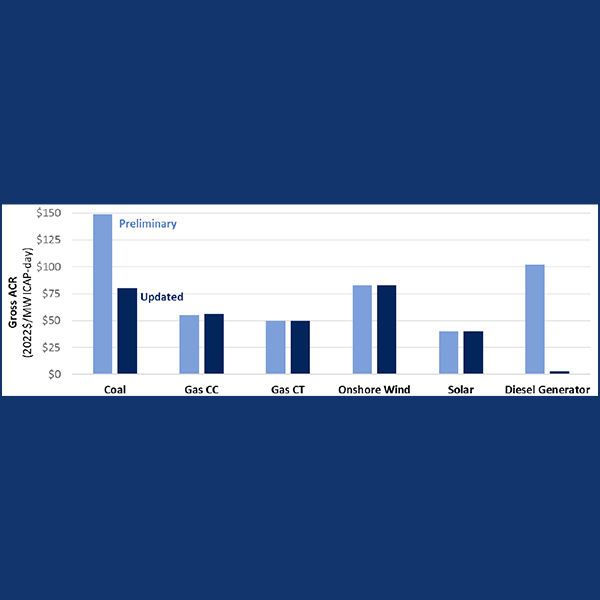
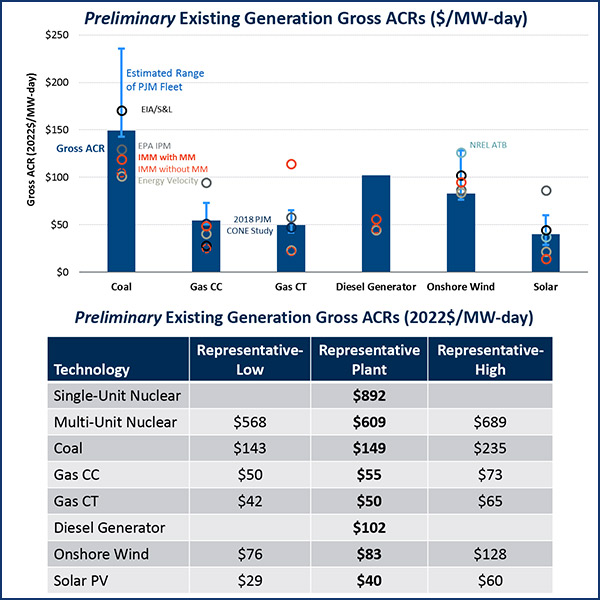
PJM officials told stakeholders that revised calculations show lower floor prices for gas, nuclear and solar generating units under the expanded MOPR.
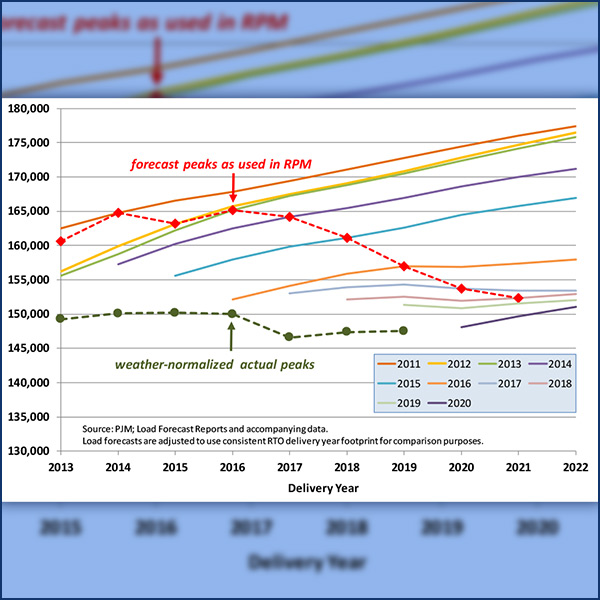
PJM’s Reliability Pricing Model is acquiring more capacity than needed, leading to dirtier, less efficient generation and excessive costs for consumers.
PJM stakeholders got their first look at the price floors that could be applied for capacity resources under the expanded minimum offer price rule.
FERC’s Dec. 19 order expanding PJM’s minimum offer price rule prompted outrage among some officials in the RTO’s 13-state footprint.
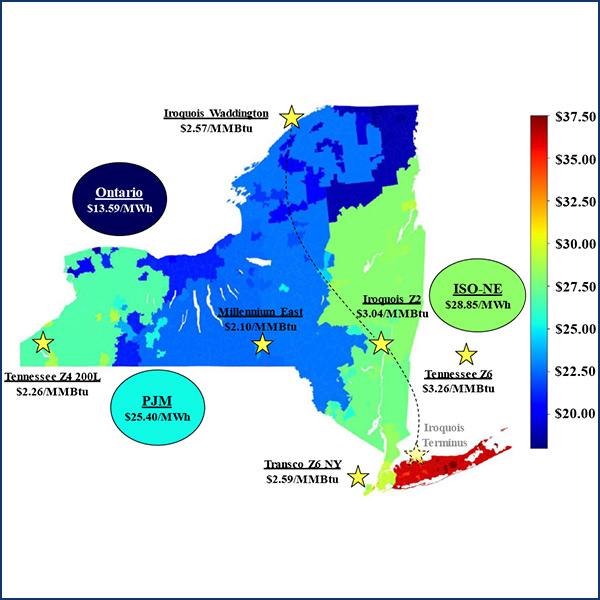
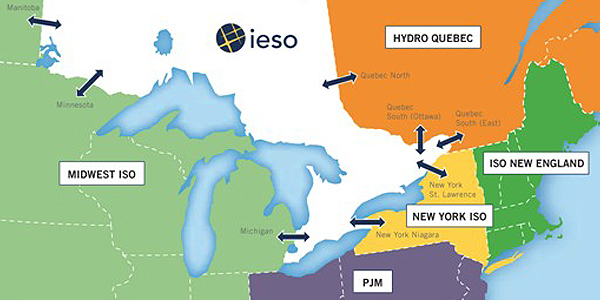
NYISO is moving the proxy bus for pricing transactions with Ontario’s IESO to reflect power-flow changes from the implementation of phase-angle regulators.
Want more? Advanced Search