The biggest obstacle to New Jersey’s adoption of clean energy is the state’s inadequate grid and a reluctance to make the kind of investments needed for the grid to handle a surge in solar and wind power, a state senator said at a clean energy conference.
Sen. Bob Smith (D), chairman of the Senate Environment and Energy Committee, which initiates much of the state’s clean energy legislation, said that despite New Jersey’s aggressive agenda, the state is far short of creating a grid that can accept numerous clean energy connections.
Smith spoke at the Clean and Sustainable Energy Summit 2024 on May 2 at Montclair University. Transmission issues were prominent, but some speakers differed with Smith’s analysis, praising initiatives such as the state’s aggressive solicitation of projects to develop onshore and offshore transmission links to connect offshore wind (OSW) projects with the grid.
Smith said his committee got some “relatively modest” climate change initiatives passed but has struggled with major initiatives to prepare the grid for the task of handling the state’s shift to an energy system focused almost entirely on electricity.
“We’re in trouble, and we’re not moving fast enough to solve the problem,” said Smith, the conference’s morning keynote speaker. He called for a “wartime mobilization for global climate change.”
“We have this 19th-century view that you should not spend an extra one-tenth of a cent in trying to upgrade your grid,” he said. The attitude is “build what you basically need and maybe only for the short term. We don’t have long-term thinking, either at the federal level, FERC, or the regional entity PJM or in New Jersey. So we now have a grid that is held together by duct tape, and not very good duct tape.”
Smith noted that Gov. Phil Murphy (D) marked Earth Week by citing his administration’s clean energy initiatives, including the allocation in his 2024/25 budget of $40 million for grid upgrades, to use a federal match. But Smith called it “literal spit in the bucket of what we need to do to make our grid work.”
In an interview with NetZero Insider after his speech, Smith said he’s uncertain whether a bill he co-sponsored, S258, which would allocate $300 million to grid upgrades to use $200 million more in federal funds, will advance in the near future. Introduced in January, the bill in March passed out of the Senate Environment and Energy Committee but has yet to move in the Senate Budget and Appropriations Committee or the Assembly.
Smith said educating legislators is not too dissimilar from educating the citizenry, in the sense they often get motivated only by a hurricane, flood or other crisis.
“People have to understand how serious this is,” he said. “We have got to get their attention.”
Marian Abdou, a commissioner of the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities (BPU), was more measured in her assessment of the state’s position. She said that “with an increase in demand for electricity and expanding our renewable energy resources, we need to ensure the grid can handle this influx.”
Standing in for BPU President Christine Guhl-Sadovy, who was unable to attend, Abdou noted the board on April 30 approved a package of grid modernization rules that could help streamline the interconnection process.
“Stable infrastructure is a critical piece of building a clean energy future, and for New Jersey, it centers on modernizing our electric grid,” she said.
Balancing New and Declining Energy Sources
Matthew Bernstein, senior policy advisory, governmental services at PJM, addressing a panel on energy security, said the RTO faces a series of the challenges but already has recognized, and responded to, the need for “proactive transmission planning,” and an improved connection process.
The RTO is working with stakeholders on a long-term framework that would allow it to get ahead of anticipated generator deactivations and load growth and focus beyond a “five-year regional transmission expansion planning process,” he said.
The RTO is addressing the ongoing backlog of new projects awaiting connection through reforms that would allow the company to “expeditiously move these projects through the interconnection queue,” Bernstein said.
“We implemented stronger guardrails around speculative projects to show that the projects that are entering the queue really do have the potential to be built,” he said. “We’re already seeing a lot of projects make their way through the queue in a much more timely manner.”
By the middle of 2025, PJM expects to have studied and processed projects with a combined capacity of about 72,000 MW, he said. And over the next three years, all 230,000 MWs of proposed projects will be studied by PJM and the response delivered to their developers, he added. Still, about 40,000 MW of generation that was passed out of the PJM connection process has not been developed due to obstacles such as supply chain issues, inflation and financial pressures, he said.
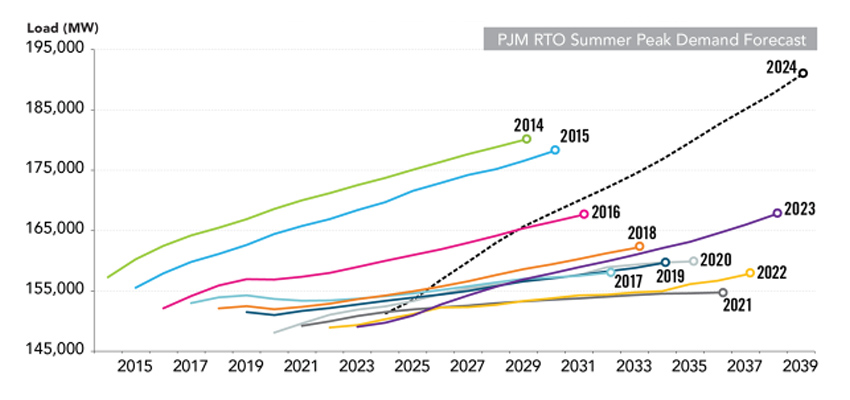
The RTO also is working to balance the retirement and closure of fossil fuel generators with the arrival of clean energy generators, to create a steady power flow that matches demand, Bernstein said. Load growth has increased dramatically, driven by “significant electrification of the transportation sector, heating equipment and other dwelling units, as well as the proliferation of data centers throughout the region.”
In its annual forecast, PJM predicted from 2014 to 2024 that load growth would decline slightly, Bernstein said. But the RTO this year predicted summer peak load will grow by about 1.7%. That dynamic has raised questions about whether the RTO has “sufficient generation available to meet our demand today, and in the future, not just the actual demand, but also have sufficient reserves in place for contingencies,” Bernstein said.
“If the load continues to grow at the rate that we are expecting, and we are seeing resources retire, this will become a problem,” he said “It’s not a problem that we’re seeing this moment today. But over the coming decade, this will become a problem if these (new) resources aren’t coming into the system in a timely manner.”
Linking OSW to the Grid
Damian Bednarz, managing director for Attentive Energy Two, which is developing a 1,342-MW OSW project off the Jersey Shore, agreed with Smith that long-term planning will be “critical” to the sector. The state has shown foresight in its “prebuild” solicitation seeking proposals for transmission infrastructure that will link OSW projects with the grid on land, Bednarz said.
If completed, Attentive Energy Two and a second project, Leading Light Wind, together would bring about 3,742 MW of capacity through Sea Girt, in Monmouth County. The projects would connect to the grid at the Larrabee Collector Station, an entry gateway the BPU instigated in a solicitation held under the FERC State Agreement Approach.
Bednarz, referring to Smith’s comment that the state needs a “wartime mobilization,” said he believes “offshore wind is that counterattack.” He added that “if we’re going to have a counterattack in this effort to combat climate change, it takes a deep level of investment into not just the generation, but all aspects, to make this reality.”
Attentive Energy was the developer of one of three projects canceled by the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA) after they had been approved in the state’s third solicitation, on Nov. 17. NYSERDA said the designated developers could not finalize their agreements due to changes in several factors, in particular a decision by GE Vernova to halt development of an 18-MW variant of its Haliade-X turbine and to remain making smaller, less efficient turbines.
Bednarz called the cancellations “incredibly frustrating” for many stakeholders, but he said the sudden, dramatic project meltdowns may be dissipating. Attentive Energy’s New York project suffered from the change in technology due to GE Vernova’s decision, rather than routine supply chain price hikes, he said.
“You also have a lot of states looking at the solicitations differently, I think, through some hard trial and error,” he said. “In key aspects of the solicitations, you have an inflation adjuster additive that could potentially push back on some of the supply chain risks, and then increased costs that can vary being factored in.“
“And I believe New Jersey, going forward, as well is going to have a lot of those things built into solicitations that prevent some of that increase in costs,” he said.



