Planning Committee
Stakeholders Endorse Quick-fix Revisions to Site Control Manual Requirements
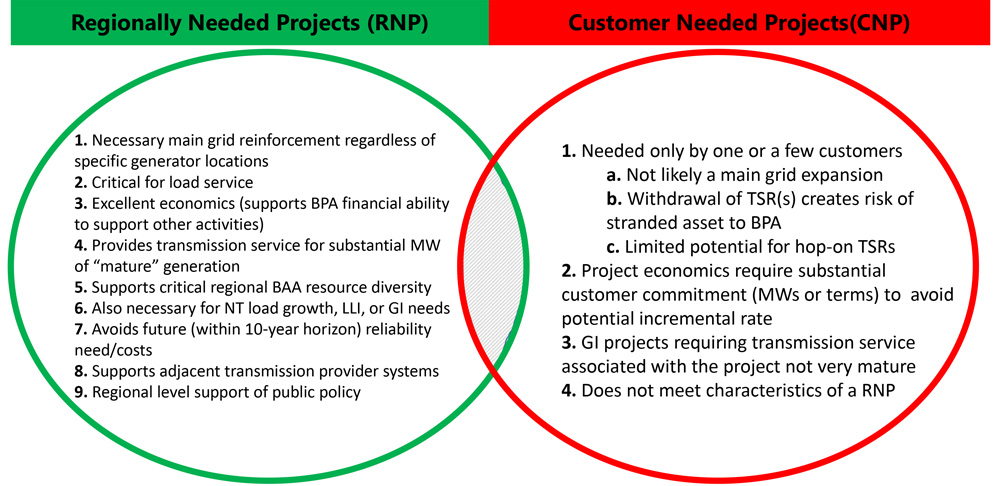
The PJM Planning Committee endorsed revisions to Manual 14H to clarify the changes developers can make to the site control requirements for their projects at different phases of the interconnection process.
Brought as a fast-track item, the proposal was voted on concurrently with the issue charge. (See “PJM Floats Fast Track Proposal on Site Control Modifications for Queue Projects,” PJM PC/TEAC Briefs: Nov. 6, 2024.)
The changes state that facility sites can be reduced so long as they continue to meet the minimum acreage and energy output provided in the project application. Developers can add parcels to a project at Decision Point 1 so long as they are either adjacent to the site or evidence of easements is provided. If the energy output is reduced, the land requirements also correspondingly would go down.
The revisions expand language at Decision Point 2 stating there are no specific site control evidentiary requirements associated with that phase to include that “site control must be maintained throughout the cycle process.” A note also would be added stating that parcels can be added similarly to DP1, with the caveat that a one-year term would be imposed from the end of Phase 2 of the relevant study cycle. Parcels also would be allowed to be removed.
No additions would be permitted at the final Decision Point 3, but reductions would be allowed so long as the acreage-per-megawatt and evidentiary requirements continue to be met. Once a generator interconnection agreement is signed, any site control changes would require a necessary study agreement (NSA) to determine permissibility.
The revisions also would correct Exhibit 10 in the manual, which inadvertently used a diagram from another exhibit when describing how generators interconnect to existing transmission substations.
PJM’s Jonathan Thompson said the revisions were drafted following stakeholder feedback seeking more leniency in site control requirements after the RTO published guidance to developers in the spring.
Preliminary Large Load Adjustment Requests for 2025 Load Forecast
PJM’s Molly Mooney presented preliminary figures for large load adjustments (LLAs) that may be included in the upcoming 2025 load forecast, expected to be published before the end of January.
Compared to the LLAs included in the 2024 forecast, the adjustments would increase from about 20 GW to about 37 GW by 2030. That figure includes LLAs that PJM expects will be accepted for the forecast, which shaves about 14.4 GW off the LLA that utilities submitted for inclusion in their forecasts. The adjustments span about a dozen zones and include data center and manufacturing loads, as well as voltage optimization projects.
“We understand this is a challenging issue because of the size of the load and the speed,” Mooney said.
James Wilson, a consultant to state consumer advocates, said PJM does not have ways of ensuring that LLA requests submitted by utilities are not duplicates of projects that are being considered at sites across multiple zones. While the estimates are likely to be accurate at least a few years out, he said it is not clear how strong the figures are well into the future, raising the possibility that there could be significant transmission buildout that consumers must pay for without assurances that it is necessary.
“We’re really left with no idea how firm this forecast is on a year-by-year basis,” he said.
Paul Sotkiewicz, president of E-Cubed Policy Associates, said more transparency is needed around how LLAs are submitted by utilities and then how PJM determines which will be included in the forecast.
PJM Seeks Stakeholder Attention on Spare Equipment Requests
PJM Executive Director of System Operations Dave Souder presented a request for the Transmission & Substation Subcommittee to review the Spare Equipment Philosophy to consider if the guidelines are adequate for extreme weather conditions that cause extended equipment outages.
The subcommittee would consider expanding the document to include equipment likely to fail during extreme weather, the feasibility of a targeted return to service that requires keeping spare equipment on hand and the logistics of delivering that equipment as part of restoration plans.
Transmission Expansion Advisory Committee
PJM Unveils Recommended Projects for 2024 RTEP Window 1
PJM plans to recommend $5.8 billion of transmission upgrades in the first window of the 2024 Regional Transmission Expansion Plan (RTEP) to allow rising demand in the east to be matched with expected generation entry in the west.
The proposal is set to go for a second read at the Transmission Expansion Advisory Committee’s Jan. 7 meeting, with Board of Managers approval likely to be sought in the first quarter of 2025.
Director of Transmission Planning Sami Abdulsalam said it should come as no surprise to stakeholders that significant load growth is driving the need for new transmission in this window, noting that similar factors have been at play in previous RTEP cycles as well. One of the aspects PJM considered when selecting proposals for the 2024 RTEP was expandability to allow additional upgrades to be added in future windows if the load growth continues.
“The 2024 RTEP Window 1 addresses accelerated load growth in various areas of the PJM footprint, changes in the mix of generation resources and the resulting shifts to regional power flows,” the RTO said in an announcement of the recommended projects. “The forecasted load growth is driven in part by data center load additions and the electrification of vehicles and building heating systems.”
The package includes a Transource Energy project to construct a new 765-kV line running from American Electric Power’s John Amos substation in West Virginia through the Welton Springs site to a new 765/500-kV Rocky Point facility in Virginia. Rocky Point would be tied into the 500-kV Doubs-Goose Creek, Doubs-Aspen, and Woodside-Goose Creek lines. Construction of the corridor from John Amos to Rocky Point would be assigned to First Energy, with Transource doing upgrades in the AEP region.
Another Transource proposal in Virginia that PJM plans to recommend would build a 765-kV line to the south from the Yeat substation through North Anna to Joshua Falls. A Dominion Energy proposal was selected to build a 500-kV loop tying a new Kraken facility into North Anna and Yeat. Transource would be assigned the southern corridor, while Dominion would construct the Kraken loop.
Transource’s southern corridor was selected in part because of its timing flexibility, with components like a new 765/500-kV Vontay substation able to be delayed until load materializes. Several substations were proposed to the north of that corridor, which PJM determined could be supplemented by the 765/500-kV Yeat facility.
Residents from Maryland and Northern Virginia spoke against the portfolio at the meeting, saying it would continue to burden residents along existing corridors and could require the taking of homes through eminent domain.
Abdulsalam stressed that PJM does not make the final route selection, which would be determined by the selected transmission developers in conjunction with state regulators.
Supplemental Projects
AEP presented a $453 million project to rebuild around 68 miles of the 345-kV Olive-Reynolds line in Central Ohio to address degradation of infrastructure along the corridor. The project is part of a larger effort to replace about 1,114 miles of paper expanded/air expanded (PE/AE) conductor in the utility’s footprint as they reach the end of their useful lives and concerns mount about core corrosion with that technology. The project has an expected in-service date of May 30, 2031.
Public Service Electric and Gas presented a $64.5 million project to construct a new Pemberton substation in New Jersey along its 230-kV Lumberton-Cookstown line. The project would address a contingency overload at the Lumberton facility, which serves 17,000 customers with a station capacity of 59.41 MVA. A peak load of 73.2 MVA was observed at the site in 2022. Pemberton would be equipped with two 230/13-kV transformers, with a projected in-service date in December 2029.
Dominion presented an $88 million project to construct two new 230-kV lines between the Devlin and Pegasus substations in Northern Virginia to mitigate a 300-MW load drop violation identified in the 2024 do-no-harm analysis. The new lines would follow a new right of way with $40 million of land acquisition expected and $33 million of line infrastructure needed. An additional $15 million would cover new breakers and equipment at the two substations. The project is in the conceptual phase with an in-service date of June 15, 2029.
Another Dominion project would build a new substation, to be named Pegasus, to serve a data center complex in Prince William County with a total load exceeding 100 MW. The $28.5 million project would cut Pegasus into the existing 230-kV lines between Hornbaker and the Pioneer and Liberty substations. It is in the engineering phase with a projected in-service date of April 14, 2027.
A $14 million project would construct a new Bristow substation along the 230-kV line from Hornbaker to Nokesville to serve a data center complex in Manassas with a projected summer 2029 load of 213 MW. The complex would be situated adjacent to Hornbaker, requiring the line to Nokesville to be re-terminated at Bristow, which then would be connected to Hornbaker with two 230-kV tie lines. The project is in the engineering phase with a projected in-service date of April 30, 2028.
Dominion also presented a $36.9 million project to build a new substation, named Meadowville, to serve a data center in Chesterfield County that is expected to see 300 MW of load by 2029. The facility would be adjacent to the planned Sloan Drive substation and would be connected by two 230-kV lines terminating into a six-breaker ring configuration. The project is in the engineering phase with a projected in-service date in the first quarter of 2028.
A co-located substation named White Mountain would serve an additional data center adjacent to Meadowville with a projected 2029 load of 100 MW. The $19 million project would be cut into the 230-kV Meadowville-Sloan Drive line and is in the engineering phase with an in-service date in the first quarter of 2028.
A 300-MW contingency violation was identified with the new Dominion substations in the Sloan Drive region, as the load would be served by two sources at the Allied and ICI substations. Dominion presented a $92.7 million project to add a third avenue for power to flow into the region by constructing a line from Meadowville, through the existing Enon substation, to Sycamore Springs. The Enon site would be expanded as part of the project, and the 230-kV Enon-Sycamore Springs line also would be rebuilt with double-circuit structures. The project is in the engineering phase with a projected in-service date in the fourth quarter of 2028.