California PUC Votes to Keep Aliso Canyon Open, for Now
California regulators voted Dec. 19 to keep the Aliso Canyon Natural Gas Storage Facility running with the goal of eventually shutting it down, saying the site of a massive gas leak in 2015 remains necessary to maintain reliability and reasonable rates.
The California Public Utilities Commission voted in favor requiring peak day demand forecasts to decrease to a target level before it can revisit the subject and investigate whether to shut down the controversial Southern California Gas-owned facility.
Regulators declined to vote on a separate proposal introduced Dec. 9 that would postpone a decision on the plan until March 31, 2025.
“This proceeding was really one of the most complex and technically challenging proceedings that has come before the commission in a while,” CPUC President Alice Reynolds said during the meeting.
The approved plan requires the CPUC to issue biennial assessments and recommendations for Aliso Canyon inventory in coordination with the California Energy Commission, Los Angeles Department of Water and Power, CAISO and the California Geologic Energy Management Division.
The commission can open proceedings to close the facility when the peak demand forecast for two years decreases to 4,121 MMcfd and the assessments show that reliability can be maintained, according to the order.
The current forecast peak demand is 4,618 MMcfd and is expected to decrease to 4,197 MMcfd by 2030, according to the CPUC. However, commissioners said the target could be reached sooner than the current forecasts project, pointing to local, regional and federal incentive programs to bring online clean energy resources and replace natural gas appliances.
The decision “puts forward a path to closure of Aliso Canyon that is achievable,” Reynolds said. “It’s realistic and protective of families and businesses who are struggling to pay energy bills. The path is not only achievable, but it could be shortened if reduction in gas demand is accelerated.”
“We share the commission’s and governor’s view that natural gas storage at Aliso Canyon is currently necessary to help keep customers’ electric and gas bills lower and for energy system reliability,” SoCalGas spokesperson Chris Gilbride said in a statement.
But critics argue the plan will keep Aliso Canyon open indefinitely and continue to put nearby residents at risk of methane leaks.
The Sierra Club on Dec. 3 contended in opening comments at the meeting that the proposal is “the latest in a string of commission failures” to close the facility in the foreseeable future. The organization added that the plan hinges on gas reductions occurring “due to unidentified climate policies” and said it minimizes the damage the leak did to communities living near the field.
After the proposal passed, Andrea Vega, senior organizer at Food & Water Watch, argued that the vote represented a broken promise by California’s leadership.
“This decision is cowardly, despicable and ultimately only kicks the can down the road,” Vega said in a statement. “Not only is this a slap in the face to the residents living near the facility, but it is a warning for all of us. We desperately need leaders who stand up to corporate greed, and Gov. [Gavin] Newsom has shown today that he isn’t that leader.”
Aliso Canyon’s fate has been controversial since a ruptured pipe poured more than 100,000 tons of natural gas into the air, leading to a blowout and sickening nearby residents. The leak was contained after four months in February 2016. The facility reopened at a reduced capacity in 2017. (See California PUC Proposes Aliso Canyon Endgame.)
Berkeley Lab: Data Centers Could Need 12% of US Power by 2028
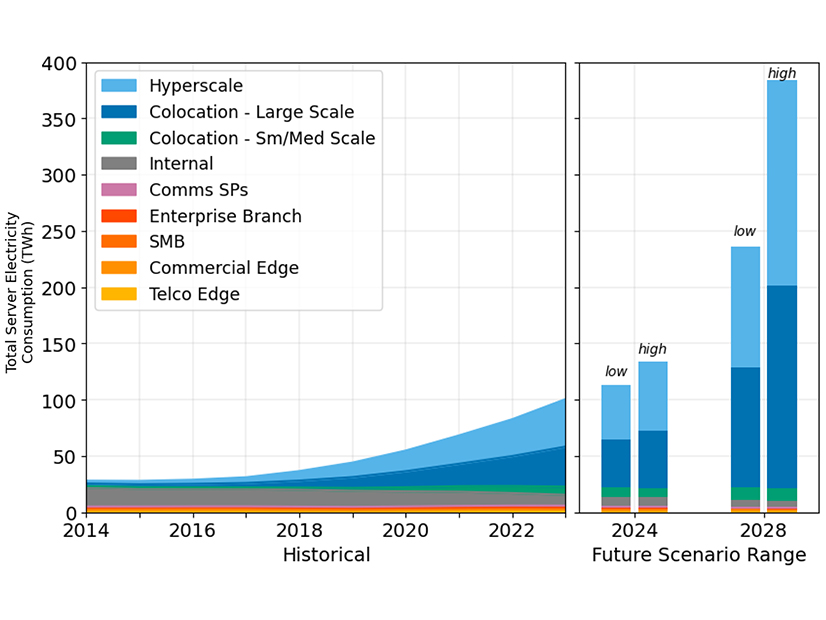
Data centers’ voracious appetite for electricity could spike more than threefold over the next four years, rising from 4.4% of U.S. power demand in 2023 to as high as 12% in 2028, according to a new report from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm said that demand can be met with clean energy. The report “crucially underscores why the Department of Energy has developed and is deploying technologies to enable continued economic growth across American industries,” Granholm said in a press release on the report.
Released Dec. 20, the 2024 United States Data Center Energy Usage Report notes that total energy demand at U.S. data centers doubled between 2017 and 2023, “and continued growth in the use of accelerated servers for AI services could cause further substantial increases by the end of this decade.”
What that means in terms of actual energy use is that data centers gobbled up 76 TWh of electricity in 2018, or 1.9% of total U.S. power demand, rising to 176 TWh in 2023, or 4.4%. Berkeley predicts future growth ranging from 325 to 580 TWh by 2028, or 6.7 to 12% of total U.S. energy demand. The power capacity required to produce that much electricity could run from 74 to 132 GW, the report says.
The report was mandated in the Energy Act of 2020 to update a 2016 data center energy use report, also produced by Berkeley.
The new study uses a “bottom-up” approach to break down data centers’ power demand into individual components. For example, energy use varies across different kinds of servers, ranging from “conventional” single- or dual-process servers to “accelerated AI” servers, which have additional processing units that can “more quickly process large quantities of calculations in parallel.”
Berkeley then drills down into the “wattage levels” of the different types of servers, including nameplate power, power for maximum computational levels and “typical” operational levels, and the “idle” power demand when the server is not being used.
“Operational power in the years 2024 to 2028 is varied between 60 and 80% of the rated [nameplate] power to reflect possible differences in the future,” the report says.
It also tracks energy use by data center type, from the smallest telecommunications servers located in closets to hyperscale centers run by tech giants like Microsoft, Google and Amazon, which have accounted for an increasing percent of demand.
Berkeley also differentiates between the power demand of AI servers used for “training” ― that is, being fed with publicly available data ― and those used for “inferencing,” which is applying those trained models for analysis or predictions. While inferencing accounted for 60% of AI servers’ power use up to 2023, the report anticipates the power demand of training servers will edge them out by 2028, rising to 50 to 53%.
When Demand Doesn’t Show up
The report argues that its bottom-up approach could be more accurate than the projections of growing data center power demand being produced by some U.S. utilities, which typically may be based on market research estimates.
“While not meaningless, historical utility demand forecasts consistently overestimate both peak and average demand,” the report says.
Such overestimates may result from including data centers that have yet to choose an electricity provider, while undervaluing the capacity of renewables, the report says. Some utilities are responding to demand growth with plans to push back previously announced closure dates for coal plants and to front-load construction of new natural gas generation.
Further, according to Berkeley, the information reported by data centers themselves does not provide the level of detail needed for better estimates of power demand.
“Very few companies report actual data center electricity use, and virtually none report it in [the] context of IT characteristics such as compute capacities, average system configurations and workload types,” the report says.
Because such data are often considered proprietary, the report calls for novel approaches to data sharing, such as “developing a repository for companies to provide energy-use data that would be anonymized and aggregated for public release.”
Meeting increased power demand also will require increased collaboration between data centers, utilities, and RTOs and ISOs. The report points to the risk for other customers if a utility builds infrastructure to meet anticipated power demand from a data center that does not show up.
Further research will be needed “to identify key risks for existing customers, data centers and utilities, explore existing contractual arrangements, and propose novel methods for risk-sharing and cost recovery,” the report says.
Another recommendation focuses on “demand bidding,” a demand-side version of RTO/ISO resource adequacy mechanisms. “Large loads would bid their future demand needs, becoming part of a demand-side interconnection queue,” the report says.
In her statement, Granholm noted DOE initiatives, such as its Onsite Energy Program, which offers technical assistance and market analysis to help large energy users deploy clean energy on-site; “so, data centers can be a grid asset rather than a burden,” she said.
But ultimately the report argues for a longer-term, broader approach to data center power demand. The current surge “should be understood in the context of the much larger electricity demand that is expected to occur over the next few decades from … electric vehicle adoption, onshoring of manufacturing, hydrogen utilization and the electrification of industry and buildings.”
“Stakeholders [should] use this relatively near-term electricity demand for data centers as an opportunity to develop the leadership and strategic foundation for an economy-wide expansion of electricity infrastructure.”
MISO Switches to In-house Load Forecasting to Gauge Soaring Demand
Facing proliferating load additions, MISO announced it has begun developing in-house long-term load forecasts after years of relying on outside help to form load outlooks.
Staff made the announcement at a Dec. 19 workshop, where they shared findings from MISO’s inaugural effort to produce a 20-year forecast. MISO previously relied on a combination of a third-party consultant and Purdue University’s State Utility Forecasting Group to prepare long-term load forecasts.
Executive Director of Market and Grid Research DL Oates said “it’s pretty clear” the load growth picture in the footprint is changing rapidly, propelled by a manufacturing revival, transportation electrification and data center growth spurred by rapid AI advances.
MISO forecasts its 638 TWh of gross energy in 2024 could grow to anywhere between 921 TWh and 1,225 TWh in 20 years, driven by data centers, electric vehicles and a burgeoning green hydrogen industry.
Executive Director of Transmission Planning Laura Rauch said MISO’s load growth forecasting will factor heavily into MISO’s three, 20-year futures scenarios, which are used to inform long-range transmission planning. The grid operator has committed to revising its futures throughout 2025 to account for more load and more clean energy transformation. (See MISO Pauses Long-range Tx Planning in 2025 to go Back to the Futures.)
MISO engineer Brad Decker said MISO and the rest of the country are exiting a roughly 15-year period of stagnant, average 0% load growth. MISO now expects annual load growth of 1 to 2% through 2044.
MISO believes load growth from electrification to be about three times higher than previously projected through long-term forecasts. Decker said the steeper growth rate over the next 20 years is due to the “gold rush” to data centers, He said MISO is gearing up for anywhere from 19 to 30 GW of new data center additions by 2040.
Within MISO, Iowa, Minnesota and Indiana will lead in data center growth, Decker said, due to availability of land, interconnection opportunities and fiber connectivity. He also noted that electric vehicles are expected to reach cost parity with gas vehicles in the next few years.
However, Decker said MISO won’t rule out an economic slowdown that could suppress growth. He said though he thinks much of the load growth will come to pass, there are some “cracks” forming through the U.S., with consumers and companies carrying higher debt. MISO also allowed that most growth in manufacturing and industry will take place post-2030 and is “highly contingent on continued policy support” through federal laws.
Decker said he expects some of the mystique around load growth from data centers to evaporate over the next few years. He said pinning down load growth from electric vehicles a few years back was similarly nebulous.
“Load has been relatively flat, but that paradigm is coming to an end,” MISO Strategic Insights Manager Dominique Davis said. She said MISO will continue researching to better understand future demands and provide “directional insights” to its members. She said MISO will incorporate the latest macroeconomic assumptions and analyses that seek to capture fast-moving industry trends.
Davis added that MISO will look for ways to add machine learning and more automation in its forecasting process, perhaps leading to programmed data exchanges with stakeholders, load-serving entities and other third parties who help shape the forecasts.
Davis also said the RTO has more work to do to understand to what extent distributed energy resources will offset load growth.
MISO is taking stakeholders’ opinions on its internal and more comprehensive load forecasting through Jan. 15.
Consumer Groups Seek Independent Oversight of Local Tx Planning
Twenty-two consumer and advocacy groups from across the U.S. filed a complaint with FERC Dec. 19 contending that the local transmission planning processes overseen by the commission demonstrate widespread inefficiencies that needlessly incur costs for electricity ratepayers.
The Industrial Energy Consumers of America (IECA), American Forest & Paper Association, R Street Institute, Public Citizen, Maryland Office of People’s Counsel, Pennsylvania Office of Consumer Advocate and other consumer groups filed the lengthy complaint against ISO/RTOs, utilities outside the organized markets and jurisdictional utilities with local planning processes.
“FERC’s stated mission is to ‘assist consumers in obtaining reliable, safe, secure and economically efficient energy services at a reasonable cost through appropriate regulatory and market means, and collaborative efforts,’” IECA President Paul Cicio said in a statement. “FERC has failed in its mission to deliver ‘just and reasonable’ transmission rates.”
He added that while the commission has required regional planning for three decades as an essential component to just and reasonable rates, it has continued to allow individual transmission owners to plan electric infrastructure critical to the nation’s economy and security based on their individual corporate interests and increasing their profits.
“Complainants demonstrate that provisions in the tariffs of the named public utilities and the RTOs/ISOs inappropriately authorize individual transmission owners to plan FERC-jurisdictional transmission facilities at 100 kV and above without regard to whether such local planning approach is the more efficient or cost-effective transmission project for the interconnected transmission grid and cost-effective for electric consumers,” the complaint said.
“Local planning, coupled with the absence of an independent transmission system planner, has produced inefficient planning and projects that are not cost-effective, resulting in unjust and unreasonable rates for both individual projects and cumulative regional transmission plans and portfolios,” it said.
FERC has a statutory requirement to protect consumers from excessive rates and charges, and is required to protect the public interest, as distinguished from the private interests of utilities, the complaint said.
“The commission has not fulfilled its statutory obligation to ensure just and reasonable, non-discriminatory transmission rates and practices affecting those rates because existing local planning tariffs allow individual transmission owners to plan FERC-jurisdictional transmission facilities at 100 kV and above without regard to whether it is the right project for the interconnected grid, resulting in unjust and unreasonable rates,” the complainants wrote.
FERC discussed the drawbacks to such local transmission planning processes in Order 1920 but did not change anything, saying such concerns were outside the scope of the proceeding that produced the transmission planning rule, they contended.
‘Shareholder Directives’
The complaint notes that PJM’s territory has 1,584 locally planned transmission projects valued at $18.1 billion with expected in service dates from Jan. 1, 2024, until Dec. 31, 2028.
“Those projects, like locally planned projects across the country, receive only a superficial, if any, independent review and thus there is no assurance that they represent efficient or cost-effective projects for consumers,” the filing said. “Importantly, this complaint does not challenge the rates for any specific locally planned project as unjust and unreasonable; instead, this complaint alleges that the cumulative effect of tariff provisions allowing local planning of transmission projects 100 kV and above results in unjust and unreasonable transmission rates.”
According to the complaint, the overbuilding is worse for smaller transmission lines from 100 kV to 230 kV, but it argues that the entire grid is being overbuilt. It contends that the “massive spike in consumer expenditures for locally planned transmission” is the result of incumbent utilities responding to “shareholder directives.”
“The investor-owned utilities do not hide this fact, repeatedly telling Wall Street analysts the amount of commission-jurisdictional capital expenditure (CapEx) expected over the coming years in order to bolster stock prices,” the complaint said. “The investor-owned utilities could only know the level of FERC-jurisdictional transmission CapEx if they also know that the jurisdictional transmission planned will inure to their rate base because they will not be subject to any competition to garner those projects, and thus exists the incentive for self-planned transmission.”
The complaint proposes to fix the status quo with a requirement that all regional planning be conducted through an “independent transmission planner” to ensure the best project for consumers and the interconnected grid is developed in the regional plan, Cicio said.
Oklahoma Gov. Stitt Threatens to ‘Unplug’ from SPP
Oklahoma Gov. Kevin Stitt’s (R) recent threat during a television interview to “unplug” from SPP may sound like political rhetoric designed to curry favor with his constituents, but the Arkansas-based grid operator is taking the statement seriously.
Calling himself the “most pro-oil and gas governor in the country,” Stitt told Oklahoma City political analyst Scott Mitchell during his local “Hot Seat” program that the “feds coming in demanding eminent domain” to build transmission lines is why he wants to “pull that back from the feds, pull back from SPP.”
“I just don’t want to have to play ‘Mother, may I’ to the Southwest Power Pool … before I add energy to my own grid,” Stitt said. “That’s where I have a problem with the Southwest Power Pool. So, I’m looking at unplugging from them.”
Stitt was apparently conflating the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Interest Electric Transmission Corridors (NIETCs) with SPP’s transmission work. One of those corridors, the 645-mile Delta-Plains corridor from Little Rock, Ark., through Oklahoma, drew strong political and public opposition in the state over eminent domain concerns.
“I won’t let anyone steamroll Oklahomans or their private property rights,” Stitt posted on X. “The feds don’t get to just come here and claim eminent domain for a green energy project that nobody wants.”
When the corridor was not included among the three corridors that advanced to the next phase, Stitt returned to X. “Good riddance. Another win for Oklahoma!” he crowed. (See DOE Cuts NIETC List from 10 to 3 High-priority Transmission Corridors.)
Still, his comments drew the attention of SPP. Staff have been working with Stitt ever since, providing a statement to Oklahoma media and clarifying that they have nothing to do with the NIETC process. They have also been working to answer a list of questions the governor has submitted to the RTO.
“We’re working to provide him the information he’s seeking, and we hope to provide that to him within the next several weeks,” COO Lanny Nickell, SPP’s newly minted CEO-in-waiting, told RTO Insider. (See related story, SPP Names COO Nickell to Replace Sugg as CEO.)
So, can Stitt unplug his grid from SPP? It would likely require legislation directing electric utilities to withdraw from the RTO. But that’s easier said than done.
First, there’s the matter of the substantial termination fees the state’s utilities would have to pay to leave SPP’s membership. Oklahoma would then have to figure out the construct under which to operate its own market and how to perform the services SPP currently provides. That would include reliability coordination, transmission planning and dispatch, crafting market rules and providing open access.
While incurring significant costs standing up a replacement to SPP, Oklahoma would also lose the benefits of belonging to a RTO, where costs are socialized among its members. The grid operator’s 2021 Value of Transmission study found that the $3.4 billion of new transmission projects placed in service between 2015 and 2019 will result in more than $27.2 billion in savings and benefits over the next 40 years, a benefit-cost ratio of 5.24.
Those numbers and other metrics are some of what SPP is providing to Stitt, Nickell said. He pointed out that every expansion of SPP’s membership has resulted from utilities, states and regulators determining that RTO membership provided significant net benefits through increased reliability, more affordable wholesale electricity and offering members’ input in developing solutions that benefit the entire footprint.
In the meantime, SPP is continuing to talk with Stitt’s office to “strengthen our mutual understanding” of how the RTO can continue to keep the state’s lights on “affordably and reliably,” Nickell said in his statement.
“We’ll continue to work with Gov. Stitt, as we do with all legislators and regulators across our service territory, to ensure the benefits of SPP membership continue to far outweigh the costs,” he said.
LPO Finalizes Major Loans to Ford, Stellantis for EV Battery Plants
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Loan Programs Office is locking in billion-dollar federal investments aimed at building out a domestic battery supply chain that could accelerate the rollout of new electric vehicle models by major automakers.
On Dec. 16, LPO announced it had finalized a $9.63 billion loan to BlueOval SK, a joint venture between Ford Motor Co. and South Korean battery maker SK On. The company is building three mammoth battery factories, two in Kentucky and one in Tennessee, which eventually will produce more than 120 GWh of batteries per year, to be used in Ford and Lincoln EV models.
The second finalized loan, announced Dec. 17 for $7.54 billion, is going to StarPlus Energy, a joint venture of Stellantis and Samsung. StarPlus is nearing completion of the first of two EV battery factories in Kokomo, Ind., with a total annual battery capacity of 67 GWh, or the equivalent of about 670,000 EVs.
BlueOval also has two of its three factories getting ready for production in 2025, one each in Kentucky and Tennessee. While the company says construction of the second Kentucky plant is “on schedule,” work on the project was put on hold in 2023 after Ford pulled back on its planned rollout of EVs because of lower-than-expected demand.
The BlueOval and StarPlus loans are, respectively, the largest and second largest that LPO has made under its Advanced Technology Vehicles Manufacturing program, which is designed to “provide low-cost debt capital for fuel-efficient vehicle and eligible component manufacturing in the United States,” according to an LPO fact sheet.
In December 2022, LPO also closed a $2.5 billion loan to Ultium Cells, the battery joint venture of General Motors and LG Energy Solutions, again to fund battery factories in Michigan, Ohio and Tennessee.
In BlueOval’s case, the loan will help the company “do more, faster, increasing liquidity and optimizing financial flexibility,” CFO Jiem Cranney said in an email to NetZero Insider.
“We have invested more than $11 billion in the construction of three 4 million square-foot facilities, installation of equipment and strategically building our workforce,” Cranney said. “This loan, which will be repaid with interest, keeps us on pace for an on-schedule start to production and allows BlueOval SK to sustain and grow our presence in the EV battery space.”
Building out a domestic EV battery supply chain is seen as increasingly important for the U.S. to successfully compete against China, which controls 70 to 90% of different parts of global battery supply chains, according to a recent analysis from the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Chinese EVs are also gaining ground in Southeast Asia and Mexico, with smaller, less expensive models, in some cases priced under $20,000.
While U.S. tariffs will keep Chinese EVs out of the domestic market at least in the near term, the loans are “essential to getting [EV manufacturers] to choose the United States of America,” LPO Director Jigar Shah told Reuters. “When you look at the competition that we have from China, it is very clear to me that they have used low-cost debt for a very long time to promote a lot of manufacturing capacity that has hollowed out many communities in Kentucky, Tennessee and other states around the country.”
US Market
A robust domestic battery supply chain is also seen as critical for raising the confidence of both automakers and consumers in a strong U.S. market for electric vehicles. Despite their large investments in battery factories, both Ford and Stellantis have been cautious, if not slow, to expand their EV offerings.
Ford continued its EV pullback in August, announcing a shift in its sales strategy to focus on the commercial vehicle market and the production of hybrid vehicles, which have seen rising sales across the auto industry. Although Ford’s Mustang Mach-E has led the U.S. market for crossover electric SUVs this year, sales of the popular model fell 10% in the third quarter, according to Ford Authority, an industry trade publication.
Tesla still leads the new EV market in the U.S., with 49.5% of sales, but Ford is second, with 6.8%, according to Cox Automotive.
Stellantis, which owns the Jeep, Chrysler and Dodge brands, only recently launched its first EV for the U.S. market, the Jeep Wagoneer S. It has also announced plans to start production in early 2025 of its new electric Dodge Charger, which the company is billing as the “the world’s first and only electric muscle car.”
Stellantis grabbed additional headlines in early December with the announcement that it is partnering with Houston-based Zeta Energy to develop lithium-sulfur batteries, which could provide greater range and faster charging times, according to the Stellantis press release.
Neither Stellantis nor StarPlus responded to NetZero Insider queries about their plans for the Kokomo factories and whether they would be used to produce lithium-sulfur batteries.
EV Chargers Plugging Along
While much uncertainty surrounds the fate of federal funding for EVs during the second Trump administration, the U.S. market continues to rack up increasing sales and steady growth.
In 2024, EVs accounted for about 8% of all new auto sales in the U.S., according to year-end figures from Cox. Fourth-quarter sales of 356,000 EVs represent an estimated increase of 12% year over year.
New EV sales for 2024 are expected to hit 1.3 million, said Stephanie Valdez Streaty, the company’s director of industry insights.
Cox is predicting that EVs will “tip over 10%” of the new car market in 2025, with “the introduction of new models, improved charging and advancements in battery technology,” Valdez Streaty said during a Dec. 17 webinar. Expanding the charging network will remain critical to overcoming consumers’ charging anxiety, which could be threatened if the funding for the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure program is “redirected or eliminated,” she said.
The NEVI program, funded with $5 billion from the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, provides formula-based allocations, typically in the millions, to states to install direct current fast chargers every 50 miles along “fueling corridors,” which typically follow interstate and state highways. To date, 171 NEVI chargers are online at 41 stations across 12 states, according to the latest figures from the Joint Office of Energy and Transportation.
The U.S. now has more than 205,000 public chargers, so EV drivers on 60% of the country’s most heavily trafficked highways can expect to find a public charger every 50 miles, the office says.
FERC Approves NERC Assessment, Seeks Comment on IBR Standards
FERC on Dec. 19 accepted NERC’s 2024 performance assessment while ordering a compliance filing in six months to explain how it will track its improvement in key areas (RR24-4).
In a separate filing issued during its last monthly open meeting of the year, the commission also proposed approving two reliability standards on protection settings and ride-through requirements for inverter-based resources (IBRs) after a 60-day comment period (RM25-3).
NERC submitted its performance assessment in July, as required by FERC regulations before it can be recertified as the ERO. (See NERC Submits Final Performance Assessment.) It covers 2019 to 2023, a time in which NERC said it strove to become a “nimbler organization while continuing to adapt to the changing needs of the electric industry.”
During the five-year cycle, the grid and the ERO Enterprise weathered the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, several major severe weather incidents, the emergence of serious cybersecurity threats to grid reliability and the ongoing shift from traditional thermal generation to renewable resources. The assessment focuses on what NERC called its accomplishments in this context, in four areas:
-
- Energy: addressing challenges arising from the changing resource mix, providing sufficient energy and essential reliability services, improving system performance during extreme weather and adding transfer capability;
- Security: addressing cyber and physical security risks;
- Agility: becoming “nimbler” in risk identification and standards development; and
- Sustainability: investing in automation, eliminating single points of failure, and strengthening the ERO Enterprise’s long-term stability and success.
NERC also evaluated the regional entities’ performance, finding that they “satisfied the relevant statutory and regulatory criteria for delegation of … the ERO’s authorities.” In a supplemental filing, NERC discussed its work to improve the efficiency of its compliance monitoring and enforcement program (CMEP) and data collection. The ERO told FERC it plans to “establish metrics on noncompliance processing to ensure the streamlined compliance exception process produces the intended efficiencies.”
FERC found that the performance assessment satisfied its regulations and that NERC and the REs met the commission’s requirements. However, the commission also noted that NERC’s supplemental filing said the ERO is considering developing new performance metrics associated with the REs’ processing times.
To help this process along, FERC specified that NERC should develop metrics to track three areas:
-
- implementation and consistence of risk-based compliance monitoring practices;
- timeliness of violation processing; and
- reduction in subsequent serious risk violations stemming from similar issues as prior noncompliance.
The commission directed NERC to submit metrics for the reliability standards development program and implementation and oversight of the CMEP in a compliance filing within 180 days of its order.
IBR Standards Proposed for Adoption
FERC’s second NERC-related order concerned reliability standards PRC-024-4 (Frequency and voltage protection settings for synchronous generators, Type 1 and Type 2 wind resources, and synchronous condensers) and PRC-029-1 (Frequency and voltage ride-through requirements for IBRs).
The commission’s Notice of Proposed Rulemaking also proposed to adopt a new definition of “inverter-based resource” into the ERO’s Glossary of Terms.
NERC filed the two standards and definition with the commission Nov. 4, along with three more standards related to disturbance monitoring, reporting requirements and event mitigation for IBRs. The standards address the second milestone in FERC Order 901, issued Oct. 19, 2023. Milestone 2 standards cover performance requirements and post-event performance validation for registered IBRs. FERC did not mention the other three standards in its NOPR.
In addition to proposing to adopt the two standards and definition, the commission also proposed directing NERC to file two informational filings after they go into effect. These relate to a provision in PRC-029-1 that allows exemptions to the voltage and frequency ride-through requirements for legacy IBRs — resources that are already in operation when the standard goes into effect. Entities would have 12 months after the effective date of the standard to request an exemption.
FERC said it is curious about “the volume of exemptions, the circumstances in which entities have invoked the exemption provision and ultimately … what, if any, effect the exemption provision has on the efficacy of” the standard. The filings would be due 12 and 24 months after the conclusion of the exemption request period and would provide information on the total number of:
-
- IBRs and their capacity for which generator owners will be subject to compliance;
- IBRs and their capacity for which GOs requested exemptions;
- IBRs and their capacity for which NERC granted exemptions;
- granted exemptions by their type (voltage or frequency) and aggregated capacity; and
- granted exemptions by IBR type and their capacity.
FERC will accept comments on the NOPR for 60 days after its publication in the Federal Register. At the meeting, Commissioners Judy Chang and David Rosner both encouraged industry stakeholders to share their thoughts so that FERC can make an informed decision.
“We’re threading the needle here, aimed at balancing the need to mitigate risk and make sure we have accurate information [and] get this decision right,” Rosner said. “So I look forward to seeing comments there.”
NJ Legislators Back 2-year Delay on Electric Truck Mandate
A New Jersey Assembly committee Dec. 12 unanimously backed a two-year delay in the implementation of the state’s Advanced Clean Trucks (ACT) regulations that would mandate escalating electric truck sales.
The Assembly Transportation and Independent Authorities Committee voted 13-0 to advance the bill, A4967, which would require that the rules adopted by the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection start “no earlier” than Jan. 1, 2027, rather than Jan. 1, 2025. Trucking executives, dealers and business groups had argued that the state has neither the demand nor the infrastructure to comply with the program.
The bill was one of two approved the same day that highlighted the growing importance of state actions in combating climate change as the transition to the second Trump administration casts a high level of uncertainty over federal initiatives to cut carbon emissions, many of which the president-elect opposes.
The two bills show legislators pushing in two directions on the climate change debate: While the Assembly committee voted to slow the ACT rules, which Gov. Phil Murphy (D) has aggressively promoted, the Senate Environment and Energy Committee voted 3-2 along party lines to advance S3545, the “Climate Superfund Act,” which seeks to impose a “liability on certain fossil fuel companies for certain damages caused by climate change.”
Both bills are far from becoming law: A4967 has not moved on the Senate side, and S3545 has yet to advance in the General Assembly. The bipartisan support for delaying the ACT rules, however, suggests that bill could advance.
Assemblyman Clinton Calabrese (D), chair of the Transportation committee and one of the bill’s sponsors, opened the hearing by reiterating his “steadfast support” for the ACT regulations. But he added that “this bill seeks to address some of the significant challenges that have arisen during this implementation period.”
Assemblyman Christian Barranco (R) said, “Electrification of the transportation sector is not a political problem, it is an engineering dilemma.
“We have a very, very difficult problem being able to serve this with the [electricity] generation that we have in place.”
But environmental groups and other ACT backers said the state has already made great strides and would not have trouble meeting the program’s sales targets. They urged legislators not to slow that progress and disrupt the certainty manufacturers and fleets need to make investments.
“Based on recent estimates, manufacturers in New Jersey have, in fact, already met their compliance for next year,” with 1,000 battery electric trucks already on the road, said Karla Sosa, New York-New Jersey project manager for the Environmental Defense Fund. “To delay ACT would be a decisive blow to New Jersey’s ability to get clean trucks that we desperately need on the road.”
Grid, Price Concerns
New Jersey in December 2021 became the third state to adopt rules based on California’s ACT regulations, which require manufacturers of vehicles weighing more than 8,500 pounds to sell an increasing number of electric trucks after 2025.
The New Jersey rules will require that by 2035, electric vehicles account for 55% of class 2b and 3 trucks, 75% of class 4 to 8 trucks and 40% of truck tractor sales. Vendors would have to comply with a system of credits and deficits based on the proportion of electric trucks that manufacturers sell in the state compared to the number of diesel vehicles they sell. (See NJ Adopts EV Truck Sales Mandate.)
The committee’s vote comes after the California Air Resources Board (CARB), facing pushback from truckers, voted to adopt amendments to its ACT rules, giving truck-makers more flexibility in reaching the goals. (See Calif. Revises Clean Truck Rules to Ease Compliance.)
Representatives of the New Jersey trucking sector ― some of whom backed the idea of electric trucks — argued at the hearing that the state is far from ready to make the major transition to electric trucks. The DEP said in October there were 143 electric class 4 to 8 trucks registered in the state, and nearly 5,000 Class 2b and 3 trucks.
Helder Rebelo, director of fleet maintenance and safety for Newark-based Daybreak Express and president of the New Jersey Motor Truck Association (NJMTA), said the industry’s “very small profit margins” make it very difficult for trucking companies to pay for an electric truck that is about three times as expensive as a $150,000 to $180,000 diesel vehicle.
“To afford that truck, we are just going to have to pass it on to the consumer,” he said. He added that the grid around his employer’s depot “cannot handle” the heavy charge needed to fuel an electric truck, and company discussions with Public Service Electric and Gas leave it unclear when the necessary upgrade might happen.
The association said supporters of the bill included South Brunswick-based Hermann Services, one of the foremost electric truck adopters in the state, which has one electric Class 8 truck and 15 on order. The company believes that the state’s infrastructure should be better developed before the rules take effect, the association said.
Because of these and other factors, demand is way below the level required in the ACT sales mandates, said Joe Cambria, owner of truck dealership Cambria Truck Center of Edison. “Customers do not want to purchase these trucks,” and under the ACT regulations, “our manufacturers will not allow us to order any diesel trucks unless we provide zero-emission credits.”
“We are hopeful, if delayed, some of these items can be addressed” to make electric trucks more “commercially viable,” he said.
If not, the rules could create a competitive disadvantage for New Jersey for dealers, said Laura Perrotta, president of the New Jersey Coalition of Automotive Retailers.
“You can go to Pennsylvania starting Jan. 1, 2025, and buy any truck you want,” she said. “In the state of New Jersey, unfortunately, the manufacturers are going to restrict allocation of diesel trucks” to those dealers that sell enough electric trucks.
Business Uncertainty
But two EV manufacturers — Rivian Automotive and Tesla — urged the committee not to advance the bill.
Zachary Kahn, senior policy manager with Tesla, said the company has planned for two years around the law and is ready to sell its Class 8 truck, which can do 500 miles and can be recharged in 20 to 30 minutes.
Tom Van Heeke, senior policy adviser at Rivian, said any delay would “create regulatory uncertainty for our industry.”
“Delaying implementation would actually make it more difficult for manufacturers to meet the requirements because it eliminates the gradual ramp up that’s built into the rule,” he said. “We’re building a business, and we’ve been counting on this regulation for several years.”
Responsible Parties
At the Senate Environment and Energy Committee, legislators supporting the Climate Superfund Act said the evidence of the need for the bill is growing.
The bill would require the state treasurer to compile an assessment of the damage to the state from climate change and determine the “responsible parties” for the greenhouse gas emissions. The legislation would create a DEP program to “secure compensatory payment from responsible parties” and disperse the funds in a grant program for “climate change adaption and resilience projects.”
Sen. Bob Smith (D), the committee’s chair and one of the bill’s sponsors, listed extreme weather events, such as Superstorm Sandy and Hurricane Ida. “The people who brought you these damages should be responsible for paying for it.”
Sen. John F. McKeon (D), the other sponsor, put the cost to the state of recovering from Sandy at $7.2 billion and said the bill is “a cost recovery tool.”
“This is about who pays for the damage that’s unequivocally directed to climate change, period,” he said. “And here in New Jersey, either the taxpayer pays or the polluter pays.”
Alex Daniel, counsel for the New Jersey Civil Justice Institute, which represents the business sector, spoke against the bill, arguing it raised constitutional concerns.
“The simple fact is, for the last 100 years, our national government [and] state governments have actively permitted and encouraged petroleum extraction and refining as part of a national energy policy,” he said. “That national energy policy has resulted in petroleum products being at the very core of our energy industry.
“The risk posed by retroactive litigation [and] liability is simple: There are settled expectations that people have that the due process protects them from disproportionate liability, particularly where you have an issue like greenhouse gases that aren’t simply an American problem.”
Ed Waters, senior director of government affairs for the Chemistry Council of New Jersey, said the bill fails to “directly address the causes of carbon emissions and consumption.”
“It goes unfairly after the companies that were refining, but the actual emissions are generated by the use of fossil fuels,” he said. Moreover, he said, “there was no law against them refining the fuels,” and the law would punish them for something they did legally.
Western Market Developers Compare Approaches to GHGs
On the surface, CAISO’s Extended Day-Ahead Market and SPP’s Markets+ will take similar approaches to accounting for greenhouse gas emissions — but important differences remain.
That was a key takeaway from a Dec. 16 webinar hosted by the Western Interstate Energy Board, where designers from both grid operators discussed how each market will deal with the patchwork of GHG pricing, accounting and reporting requirements across different Western states.
While California and Washington are currently the only two states with active carbon pricing policies, several others have carbon reduction goals and other climate regulations that utilities must meet.
That leaves EDAM and Markets+ with a common goal: to implement GHG tracking and reporting in a way that accounts for different approaches to reducing emissions.
CAISO’s Approach
Developing a GHG accounting mechanism for EDAM “wasn’t necessarily a new challenge” for CAISO because California has had a cap-and-trade program in place since 2014, Anja Gilbert, a lead policy developer at the ISO, said during the webinar.
But despite CAISO’s experience dealing with GHG accounting, it faces some new challenges in accounting for emissions in EDAM, particularly involving how to track emissions in states that don’t price carbon.
Key among those challenges is implementing a market mechanism that ensures a state or load-serving entity is only served by generation that meets a certain emissions threshold.
“This is really relevant for states that have climate policies not based on the price of carbon but might have reduction goals over time,” Gilbert says. “There’s a question of if that does need to be reflected in the market.”
Another challenge has to do with unspecified imports being valued at an unspecified emissions rate.
“It doesn’t provide that level of clarity in terms of what generation is really serving that load,” Gilbert said. “That high emissions rate could undermine showing progress toward an entity’s climate goals.”
In response to those challenges, CAISO has proposed to create a residual emissions rate, which would represent a dispatch-weighted average emissions rate of the market supply and allow market participants to reflect and account for the energy and associated emissions for which they’re responsible. Under this framework, leftover energy in the market would go into the residual supply and the emissions rate would be the average of the residual mix.
To respect state preferences, the market’s optimization won’t incorporate GHG costs outside of California and Washington, but CAISO’s market design does incentivize generators to make supply available to those states. For example, if a solar resource in Arizona wants to serve load in California and receives a GHG award, the generator is paid the marginal GHG price paid for by California load.
SPP’s Approach
Over the past year, SPP has been in the process of developing a design for GHG tracking and reporting, and it provided an overview of its approach, which is similar to CAISO’s.
Gentry Crowson, a lead market design engineer at SPP, said the Markets+ GHG framework rests on two “pillars” of pricing design and a tracking and reporting service.
“These two pillars are really going to enable the footprint to be respective of state programs that are in place, as well as with state GHG reduction goals that are also in place,” Crowson said.
SPP’s GHG tracking and reporting “vision” aims for comprehensive reporting through the centralized Market Emissions Tracking and Reporting (METra) application, Crowson explained. The system’s design intends to give Markets+’s load-responsible entities (LREs) the right to claim resources and energy they own or have contracted for, in addition to ensuring that the market accounts for all generation and associated emissions in one way or another.
The first step in SPP’s design approach is called the “mapping” step, where LREs’ registered resources are modeled in a commercial model and matched to a corresponding resource portfolio. In the second step, reporting entities have the option to bring in or send out other resources by submitting them into the METra portal. The third step is to establish a contract between the buyer and seller that is then reflected into LREs’ resource portfolios.
After the market runs and market operators and participants have a better understanding of the actual output, any generation that exceeds the load amount is deemed excess energy and is allocated to a residual energy report, similar to CAISO’s method.
“Once the market runs and you’re looking at a load-responsible entity’s resource portfolio, if that load-responsible entity has any excess energy, we had to come up with options to figure out how to calculate this residual energy pool as we pull together these emissions,” Crowson said.
The Markets+ GHG Task Force unanimously endorsed the tracking and reporting design in September, and the Markets+ Participants Executive Committee approved it in November.