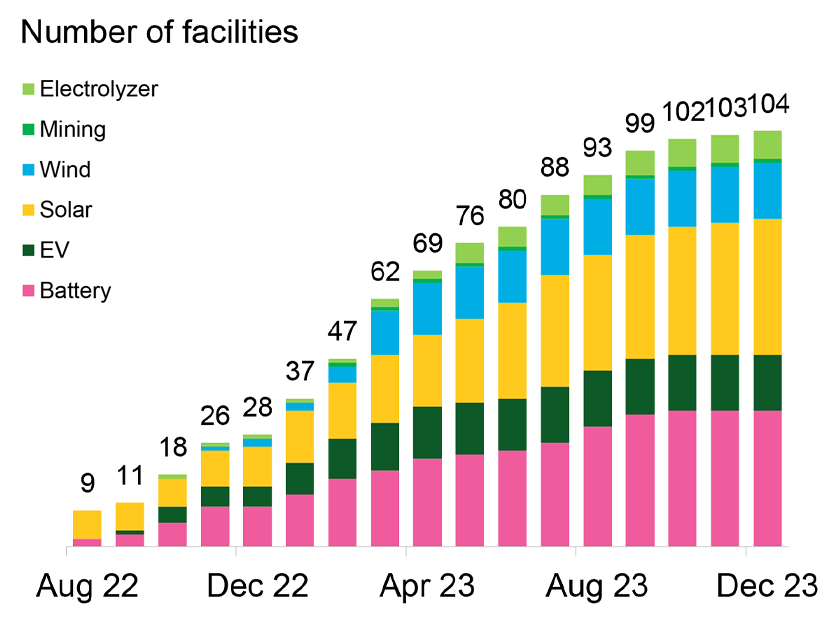
The New York Power Authority (NYPA) and the New York University Tandon School of Engineering on Feb. 22 announced a partnership that could help state utilities prevent costly and time-consuming large power transformer outages through a novel monitoring technique.
NYPA will test NYU Tandon’s “Online Detection of Winding Deformations in Large Power Transformer” study at its Advanced Grid Innovations Laboratory for Energy (AGILe) simulation facility to assess if the school’s technique can be scaled up for the wider New York grid to improve the detection of transformer-winding deformations without statewide interruptions.
“NYU Tandon aims to integrate into NYPA’s AGILe processes by developing a comprehensive model encompassing various common deformations in transformer windings,” Shayan Behzadirafi, a project engineer on NYPA’s Research, Technology Development and Innovation team, told RTO Insider.
The partnership, supported by a nearly $190,000 grant from the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority’s Future Grid Challenge program — itself funded through the nearly $2.4 billion Clean Energy Fund — aims to digitally monitor NYPA’s large-scale transformers by continuously tracking the voltage and currents of transformers while accurately calculating its leakage impedance (14-M-0094).
“The idea is to scale up the technique, which was tested with a 1-kVA lab transformer, to the NYPA large transformers of hundreds of megavolt-amperes,” Francisco de Leon, a NYU Tandon professor of electrical and computer engineering and one of the study’s authors, wrote in an email to RTO Insider. “If the project is successful, the condition-monitoring device will save money in unnecessary tests when the transformer is healthy or prevent catastrophic failures when the transformer has been damaged.”
NYPA estimates that if the technique prevents many of the diagnostics required once a transformer is taken out of service because of winding deformations, the state could save about $15,000 per day and up to $1.5 million per incident.
“Basically, what we are doing for transformers is giving them a smartwatch,” de Leon said in an interview with RTO Insider. “It is something that is monitoring all the time and giving real-time analysis of some of [the transformer’s] components without having to disconnect the transformer.”
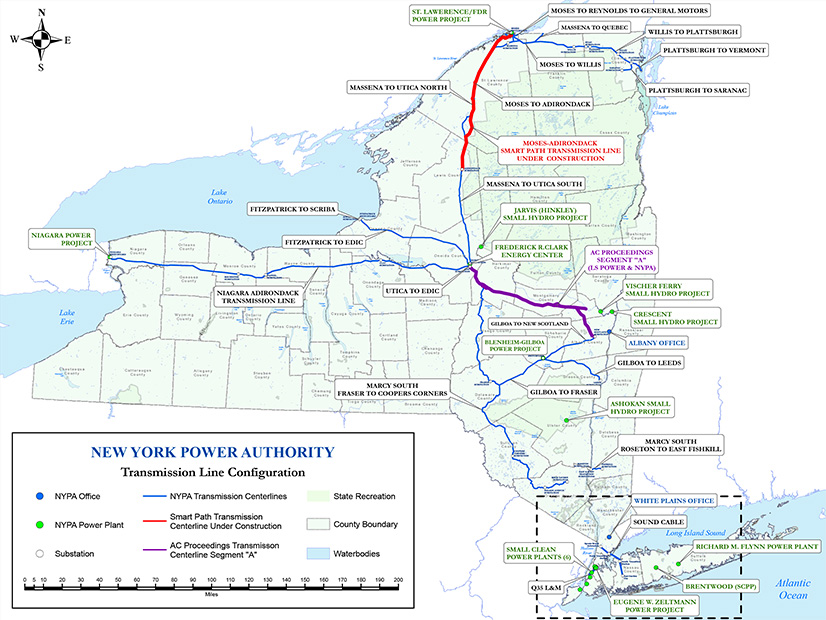
This has big implications for NYPA, the largest state public power organization in the U.S., as it operates more than 1,400 circuit-miles of transmission lines, has 16 generating facilities — including the hydroelectric Niagara Power and the St. Lawrence-FDR Power projects — and produces more than 80% of its electricity from renewables.
Transforming the Future
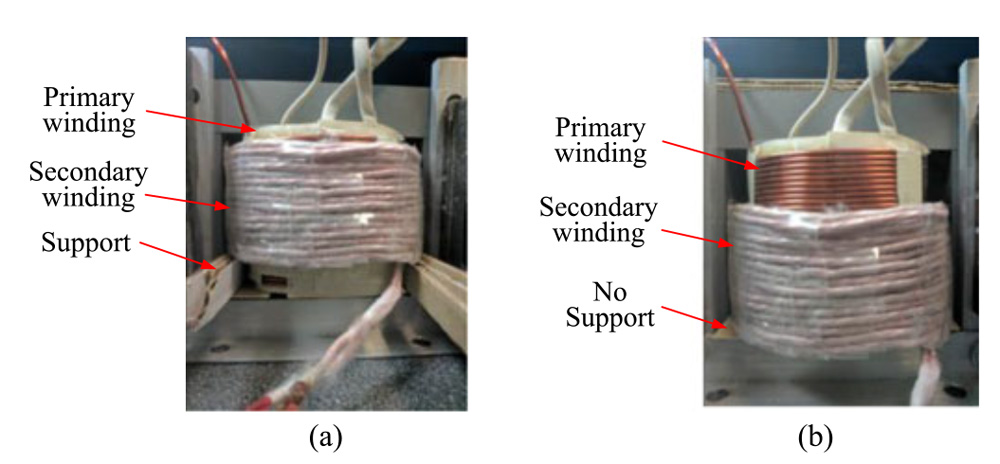
NYU Tandon’s paper, published in the journal IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery in 2018, emphasizes how transformers’ windings, which consist of metal coils wound around the transformer’s core, “are subjected to strong electromagnetic forces” that can cause deformations.
“To avoid crucial damage, it is necessary to detect winding deformation at an early stage,” the paper reads.
New York has experienced transformer-related outages, explosions and fires, often because of equipment failures, which led to extended disruptions and costly repairs.
Notable incidents include the December 2018 transformer explosion at a Consolidated Edison plant in Astoria, Queens, which painted New York City’s skyline bright blue. A 2021 incident captured on video in which a man in Queens survived a transformer explosion directly beneath him, and in January, another Con Ed transformer in Queens reportedly exploded, knocking out power for hundreds of customers for hours.
Transformers with deformed windings are typically taken out of service for a frequency response analysis to test the mechanical integrity, but the technique being studied at AGILe could reduce the frequency of these occurrences and the need for such service interruptions.
“Traditionally, bringing transformers out of service for frequency response tests is the norm,” Behzadirafi said. “However, if NYU Tandon’s methodology proves successful, it would eliminate the need for such disruptive measures.
“By enabling the detection of transformer issues while the unit remains in service, the study offers a substantial improvement in minimizing downtime, increasing efficiency and enhancing the overall reliability and performance of the energy infrastructure.”
New York Stays AGILe
Launched in 2017 in Albany, AGILe is described as a “a global center for electric grid research,” responsible for developing and testing “new and off-the-shelf clean energy technologies” to strengthen the state’s electric grid by fast-tracking their commercialization.
It also helps utilities better understand the potential impacts of new technologies or techniques on the state’s grid.
“Through this study, we hope to be able to give utilities confidence that this technique is reliable and will work for full-size transformers in the field,” said Alan Ettlinger, NYPA’s senior director of research, technology development and innovation.
Behzadirafi elaborated on how NYU Tandon’s developed prototype would be evaluated. “Leveraging AGILe’s hardware-in-the-loop facilities, we will test the developed hardware against the deformation models to assess its performance and ensure its effectiveness in real-world applications.”
“NYPA will conduct the study by evaluating whether the developed hardware can effectively detect various winding deformations using information provided by the software model,” he said. “The success of the study will be determined by the alignment between the outputs generated by the software model and the actual data obtained from the transducers, as well as hardware’s ability to detect, ensuring that the hardware reliably detects winding deformations in practical applications.”
The prototype being assessed by AGILe identifies changes in short-circuit impedance, a key transformer health indicator, using advanced techniques like Lissajous curve methods to track winding deformations in real time.
If found to work, the digital tool will detect emerging transformer winding deformations caused by stress from short-circuit events and send a warning alarm to an operator informing them the unit has a leakage reactance higher than the standard 3% recommended by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
“If the outcome of this collaboration proves successful, NYPA is considering a potential second phase, which involves implementing the detector relay in conjunction with a real transformer,” Behzadirafi said. “Additionally, there is a possibility of engaging popular relay manufacturers to contribute to the development of the relay during the practical phase in the real-world scenario.”
“My dream,” NYU’s de Leon said, “is that our technique is found to be successful and viable, since then we can partner with a relay manufacturer to produce a new relay prototype that is equipped with our tools and is then commercialized.”
“Unique research collaborations like this one with NYU Tandon, supported by NYSERDA, enable the Power Authority and New York state to innovate and modernize its electric grid for the benefit of all New Yorkers,” NYPA CEO Justin Driscoll said.