Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
The NYISO Operating Committee approved revisions to the 2024-01 Expedited Delivery Study, finding that all nine proposed projects are deliverable at their requested capacity resource interconnection service levels.
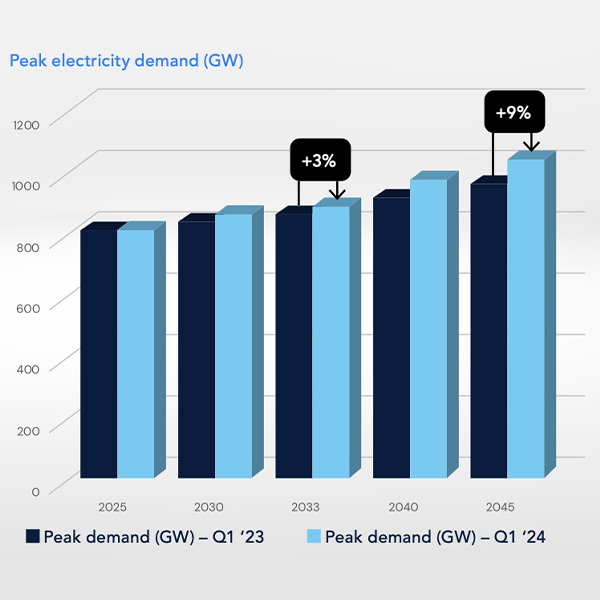
ICF International forecasts that demand could increase by 9% by 2028, while peak demand could increase by 5% over the same period, according to a report it published.
FERC is still working to implement the changes to its generator interconnection rules from Order 2023, but it is also considering further changes, as it held a two-day workshop to gather more input.
An emergency alert urging the public to conserve energy helped the Alberta Electric System Operator narrowly avert rolling blackouts during January’s extreme cold snap.
Assembly Bill 2368 would require the California Public Utilities Commission to adopt a 1-in-10 loss of load expectation — or a similarly robust planning standard — when setting resource adequacy requirements.
NYISO's update to its draft Reliability Needs Assessment still shows an expected capacity shortfall by 2034, though it is slightly less than what was initially presented in July.
Now that SPP has set planning reserve margins for the 2026 summer and 2026/27 winter seasons, the grid operator has turned its attention to setting up a longer-term PRM.
The NEPOOL Participants Committee voted to update the Generation Information System to enable the transfer of hourly certificates, opening the door for the sale of hourly renewable energy credits.
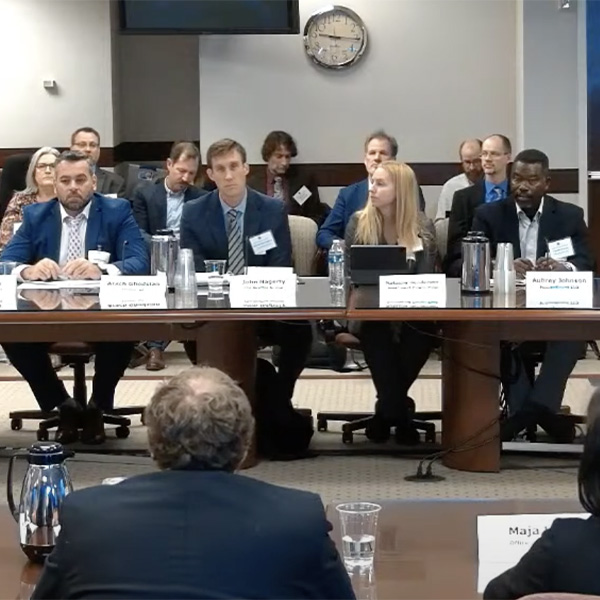
Collaboration among stakeholders will be crucial to maintaining Western grid reliability in the face of increasing demand posed by large loads such as new data centers, speakers said during a webinar hosted by WECC.
MISO is adamant that it should limit project proposals in future queue cycles to 50% of annual peak load to moderate its 300-GW, oversaturated queue.
Want more? Advanced Search