Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
New England governors asked Secretary Granholm to consider waiving the Jones Act for LNG imports and tapping the Northeast oil reserve for heat this winter.
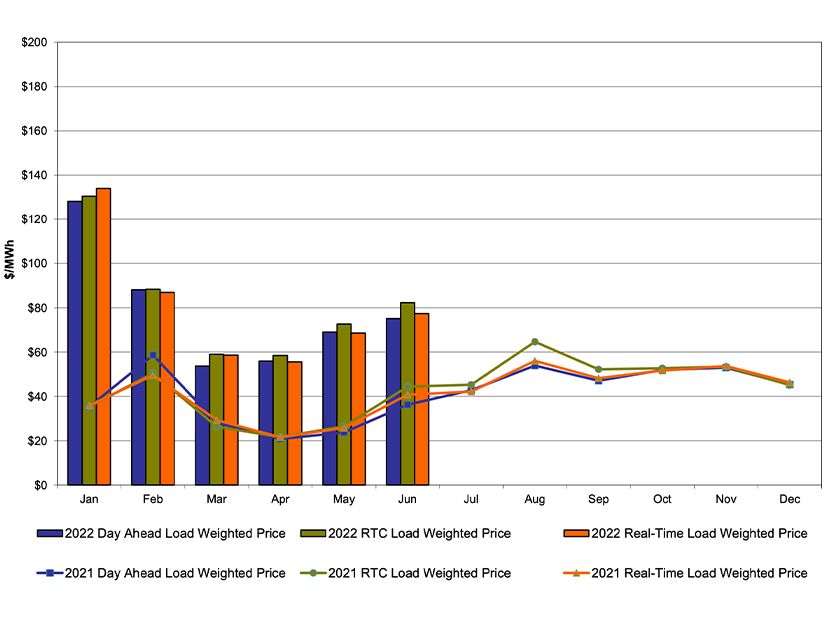
SPP’s Western Energy Imbalance Service market saw “very limited growth” in its first 13 months, SPP’s MMU said in its first annual report on the market.
San Diego Gas & Electric and its partners launched the first interconnected vehicle-to-grid project to offer support during energy emergencies.
SPP’s Board of Directors approved stakeholders’ recommendation to issue a notification to construct a 345-kV double-circuit transmission project in New Mexico.
The New York grid performed well in the summer’s 1st heat wave July 20-24, NYISO vice president of operations Aaron Markham told the NYISO Management Committee.
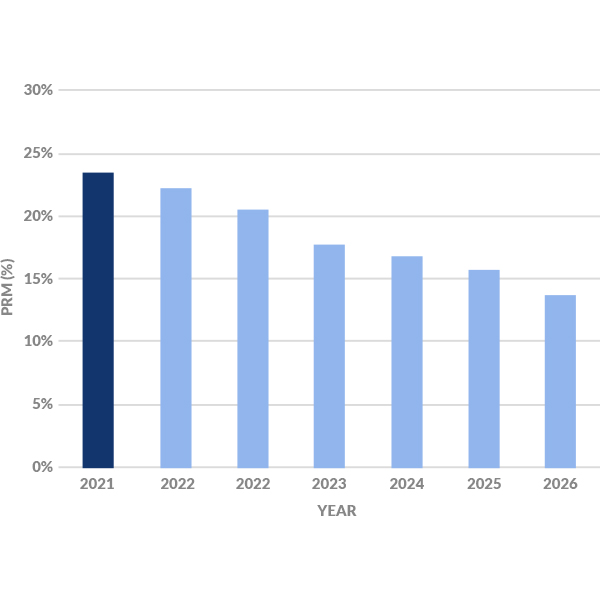
SPP’s Board of Directors has sided with staff in approving an increase of the RTO’s planning reserve margin to 15%, effective next year.
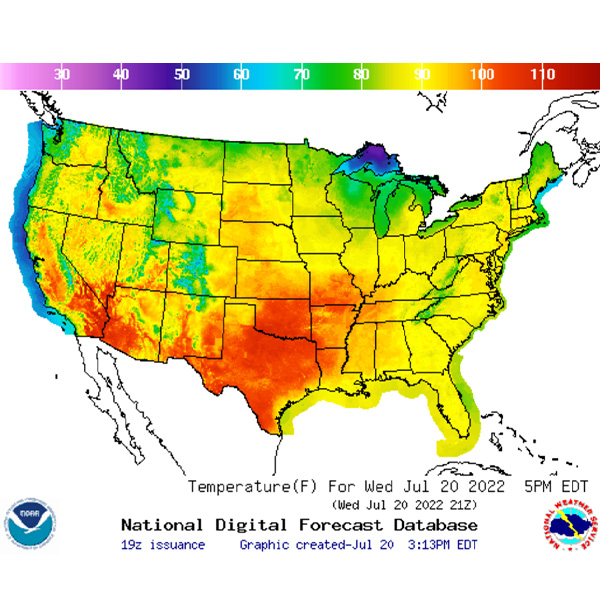
Persistent triple-digit temperatures across much of Texas have forced ERCOT to issue yet another operating condition notice as it flirts with 80-GW demand.
Sponsors of Illinois’ Climate and Equitable Jobs Act held a news teleconference to condemn “foot dragging” by MISO in getting new renewable energy online.
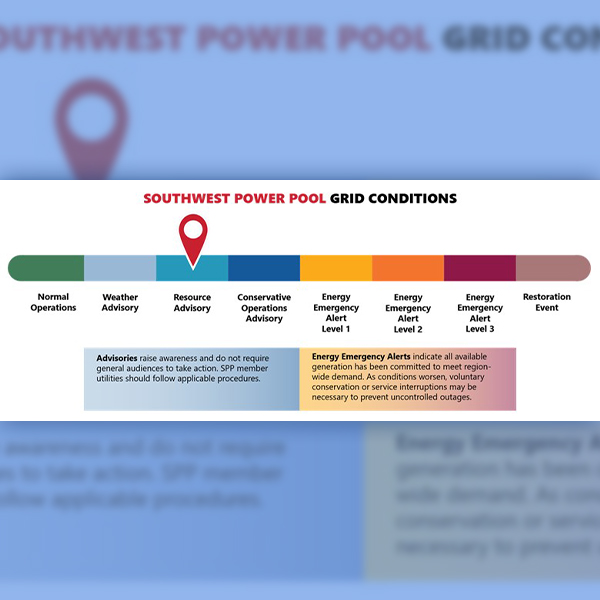
SPP has again declared a resource advisory for its footprint July 25 as searing heat continues to roast the Southern Plains.
ERCOT demand set a new demand mark for the 11th time this year as a heat dome over the Southern Plains continues to produce record-breaking temperatures.
Want more? Advanced Search