Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
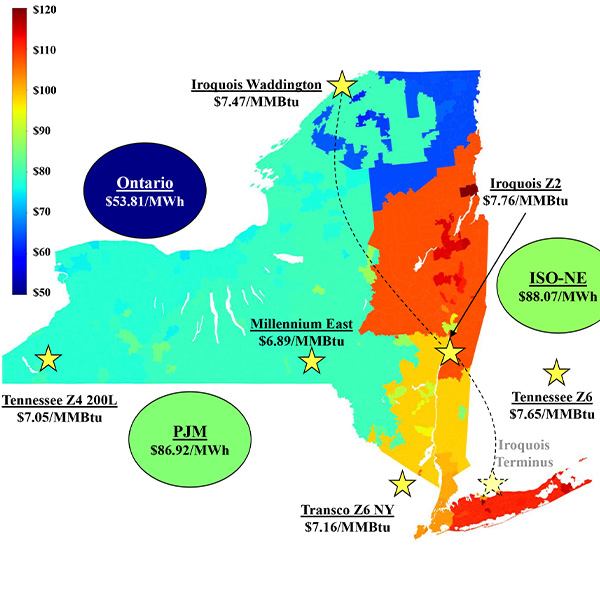
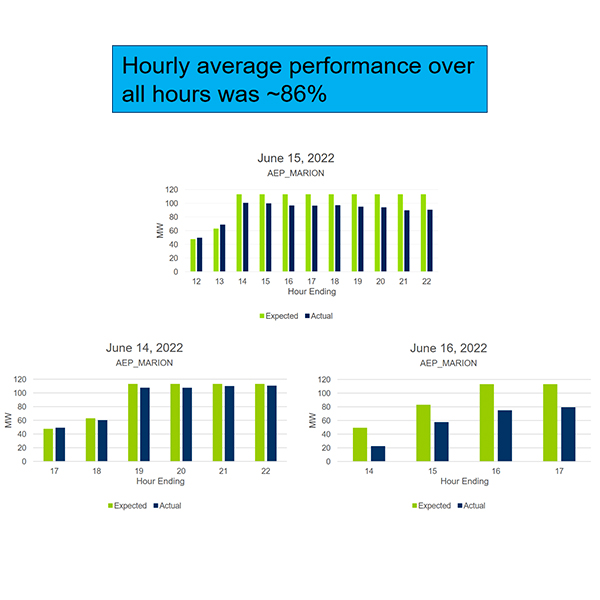
NYISO is qualifying generation units for meeting their reserve requirements even though they fail to provide adequate reserves during normal market operations.
The OC rejected modifications to its issue charge exploring costs for generators deemed critical to maintaining interconnection reliability operating limits.
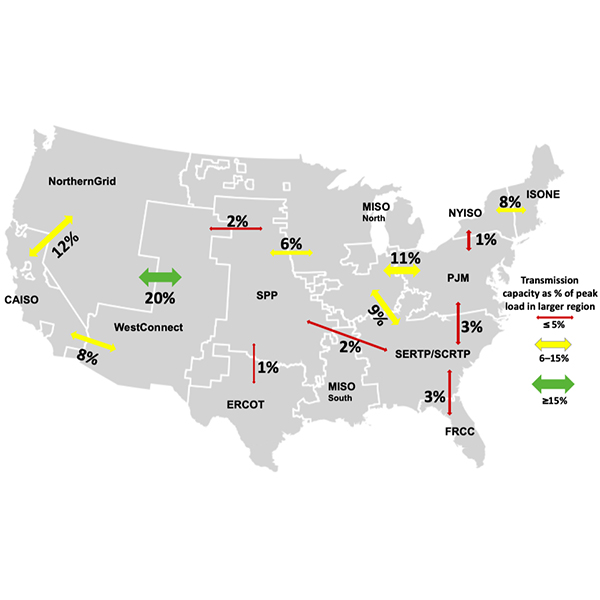
In a workshop, FERC commissioners and stakeholders debated the pros and cons of requiring minimum transfer capability between regions to promote reliability.
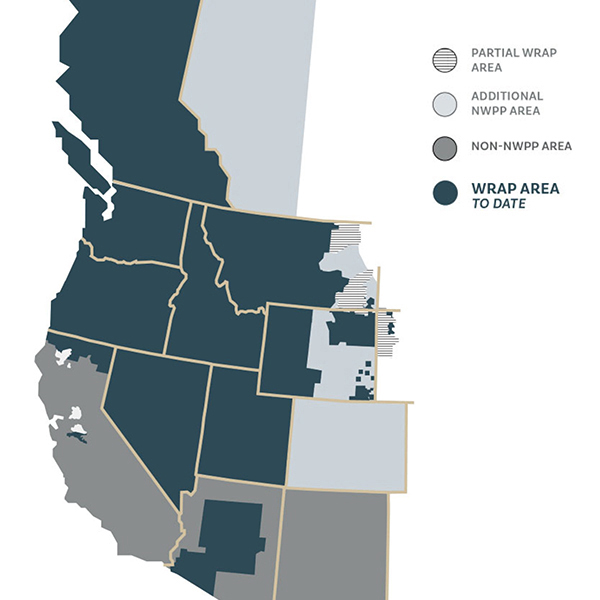
Nearly a dozen utilities committed to joining the “binding” iteration of the Western Resource Adequacy Program, with more expected to sign on later this month.
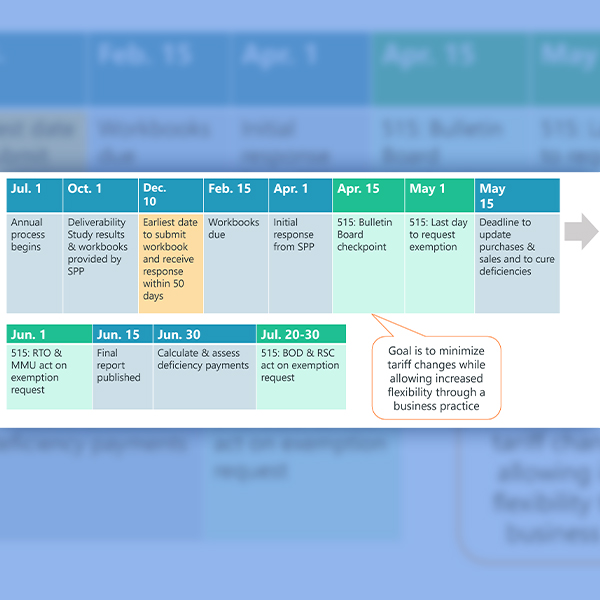
SPP staff are finalizing a mitigation strategy for load-responsible entities unable to meet the grid operator’s new 15% planning reserve margin.
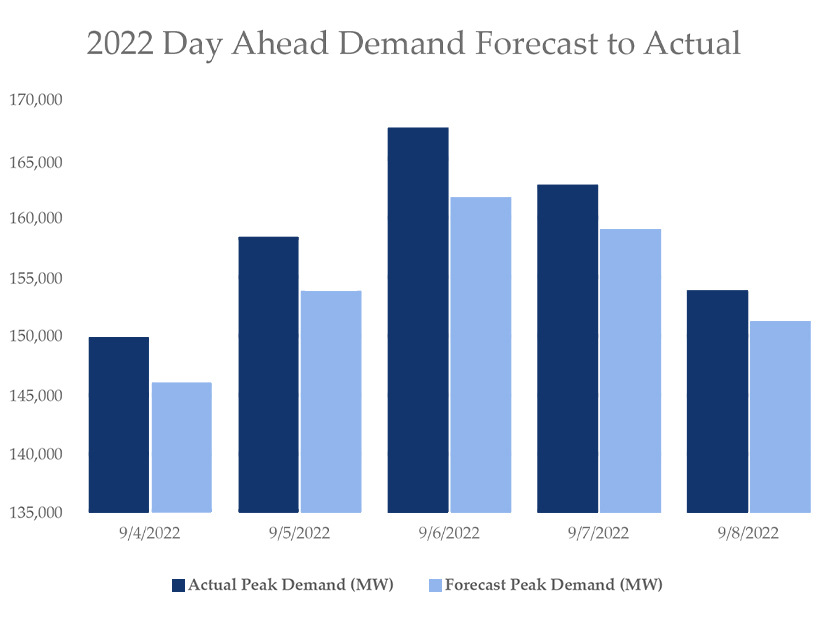
WECC directors said that Westerners should take cold comfort from the fact that grid operators were able to avert blackouts during a September heat wave.
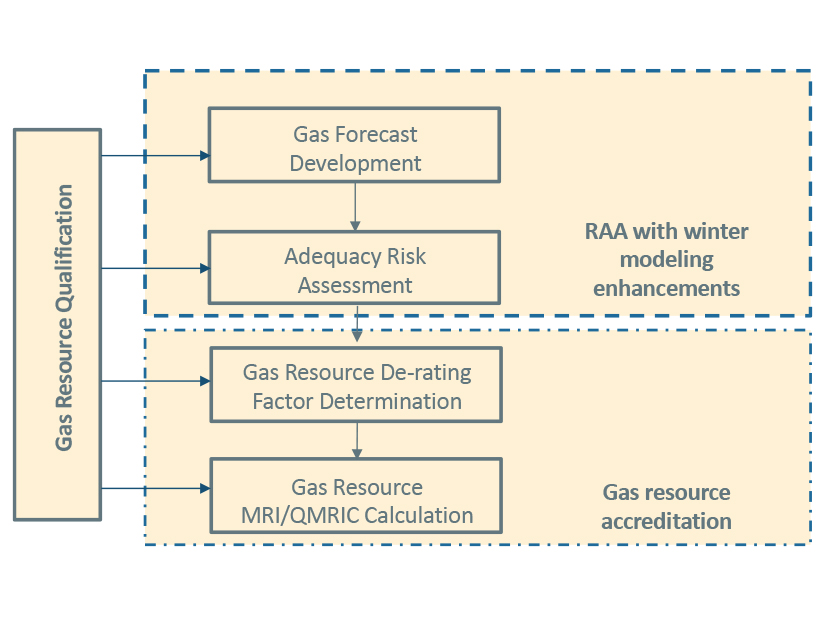
As ISO-NE continues to hack away at the complicated process of updating its capacity accreditation method, the grid operator is turning its attention to gas.
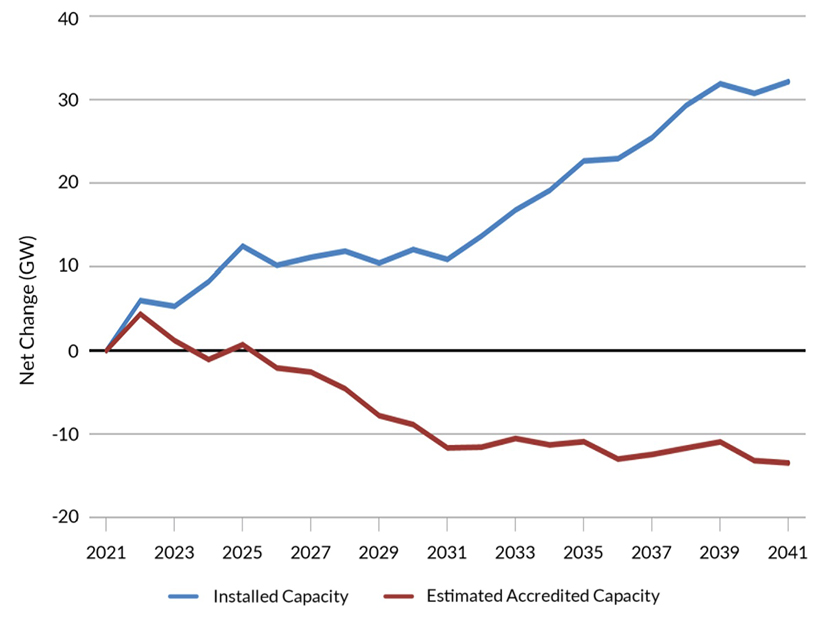
MISO said its members may need to build up to 200 GW in new installed capacity by 2041 to meet reserve requirements while achieving renewable targets.
NYISO’s Management Committee approved tariff revisions and received briefings on the ISO’s winter supply outlook and its updated Strategic Plan.
FERC asked for more information on the Western Resource Adequacy Program, including how it would accommodate participants without market-based rate authority.
Want more? Advanced Search