Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
NYISO on Monday updated the Operating Committee on January operations performance and how the early-February cold snap event impacted the grid.
NEPOOL's Markets Committee approved changes to the Inventoried Energy Program intended to get the winter reliability program in line with global energy markets.
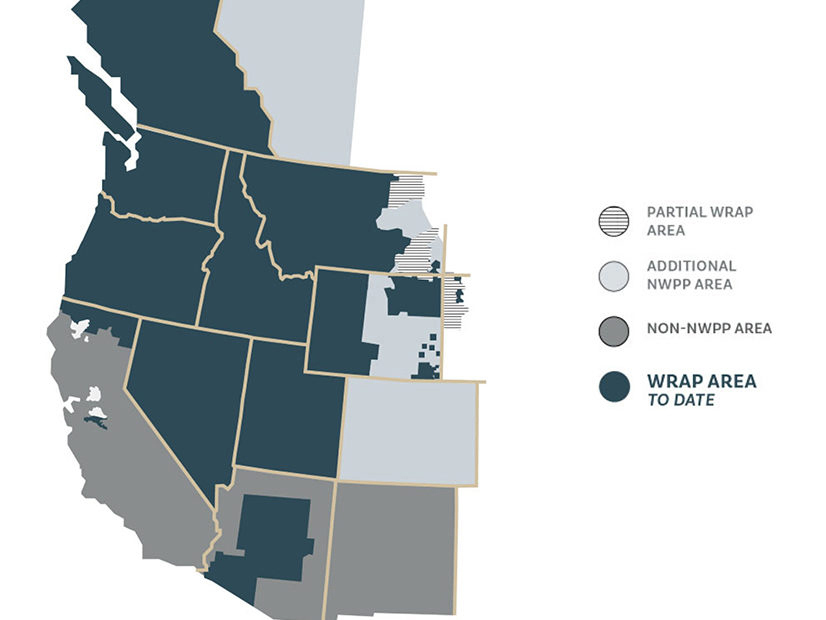
FERC approved the tariff for the Western Power Pool's Western Resource Adequacy Program, allowing the binding phase of the program to commence in 2025.
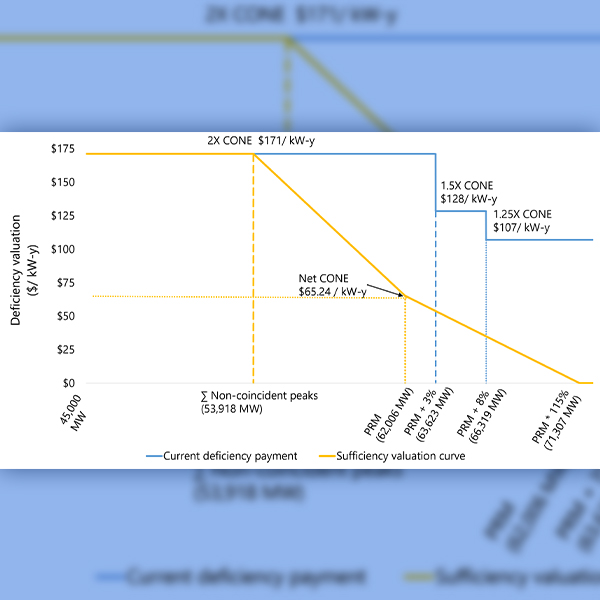
The electric sector must fundamentally reconsider how it measures and manages grid reliability, speakers on a WECC panel said.
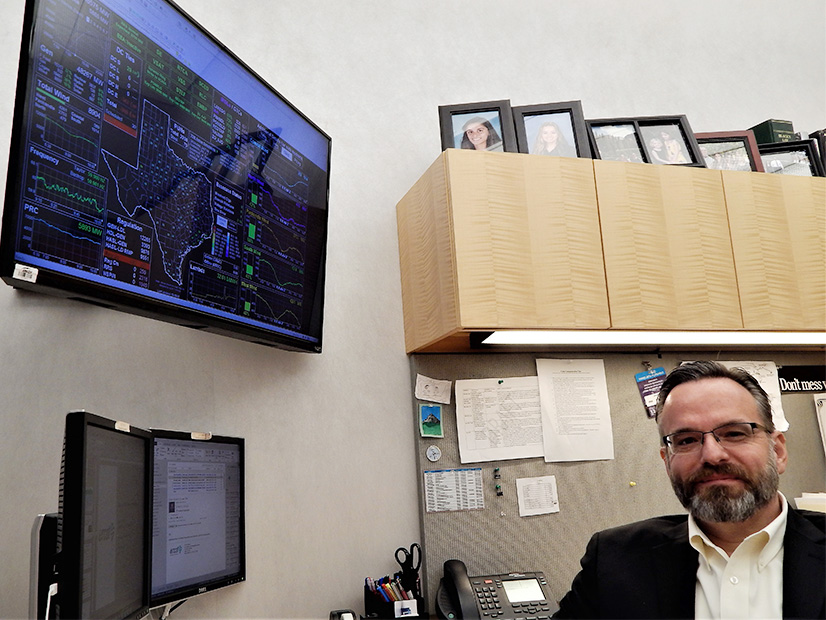
Icy weather knocked more than 400,000 Texas customers offline last week, but all outages were at the local distribution level.
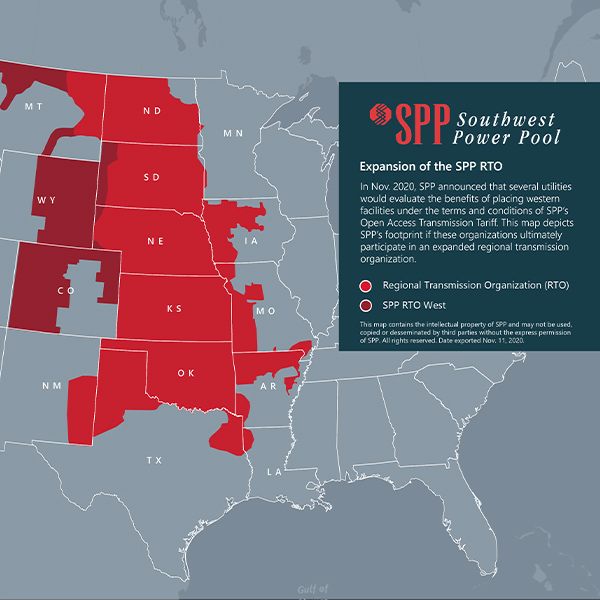
SPP’s Board and Members Committee have approved two resource adequacy revision requests, ending a last-minute dash to gain stakeholder approval.
The push for decarbonization will transform Washington from a key exporter of electricity to a net importer by mid-century, a state agency has found.
ERCOT is analyzing information from generators that were forced offline during the December winter storm to better understand why thermal outages were an issue.
SPP’s MOPC approved two revision requests related to resource adequacy requirements that members had set aside during its meeting earlier this month.
SPP and MISO plan to apply for grants from the Department of Energy to help fund five transmission projects recently identified in their JTIQ work.
Want more? Advanced Search