Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
Transmission upgrades that are needed to avoid overloads in a fully electrified New England by 2050 could cumulatively cost between $22 billion and $26 billion, ISO-NE told its Planning Advisory Committee.
NYISO did not identify any new near-term reliability issues in its third-quarter STAR, but it does anticipate significant load increases in western and central New York that could warrant more attention.
The NYSRC Executive Committee approved the modeling assumptions for its 2024/25 installed reserve margin requirement study base case and discussed potential cap-and-invest updates.
Comments are due Nov. 3 on PJM’s proposal, which it said would improve reliability and incentivize resource development while controlling costs.
NYISO gave summer and monthly operation updates during the OC meeting, and stakeholders recommended the approval of the draft annual Comprehensive Reliability Plan.
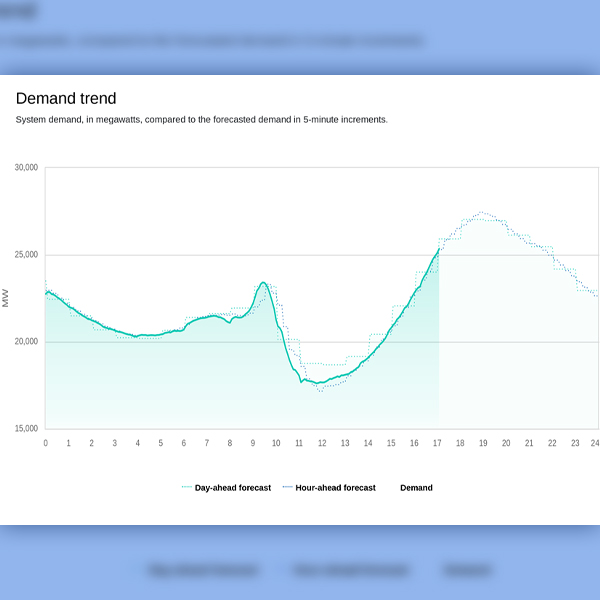
CAISO maintained normal grid operations during the Oct. 14 solar eclipse, with swings in solar production that were more muted than models based on clear-sky conditions.
California utility regulators voted to launch a proceeding to establish rules and requirements for the state’s resource adequacy program from 2025 to 2028.
A major focus at the Energy Bar Association meeting was on how to ensure reliability and affordability as the grid transitions to a cleaner future.
The PJM Market Implementation Committee endorsed the creation of a fifth cost of new entry area for the Commonwealth Edison zone, as well as two proposals aiming to limit the prospective performance impact of implementing multi-schedule modeling in the market clearing engine.
MISO said it will push back a contentious filing for a new, marginal approach to capacity accreditation into early next year.
Want more? Advanced Search