Resource Adequacy
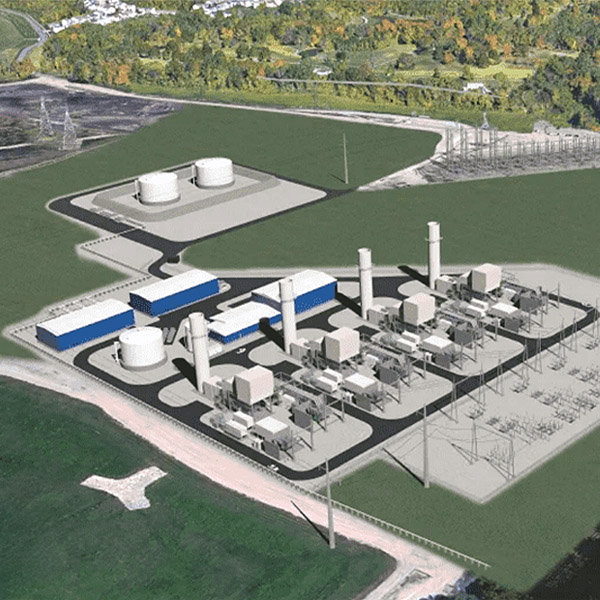
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
FERC refused MISO’s first attempt to enact a special pathway in its interconnection queue for generation projects labeled necessary by state regulators.
MISO CEO John Bear put a positive spin on the grid operator making do with little cushion in its supply.
Ohio's governor signed into law a major reform of how the state regulates utilities, eliminating electric security plans that utilities have used to meet demand from non-shopping customers since a 2008 law authorized them.
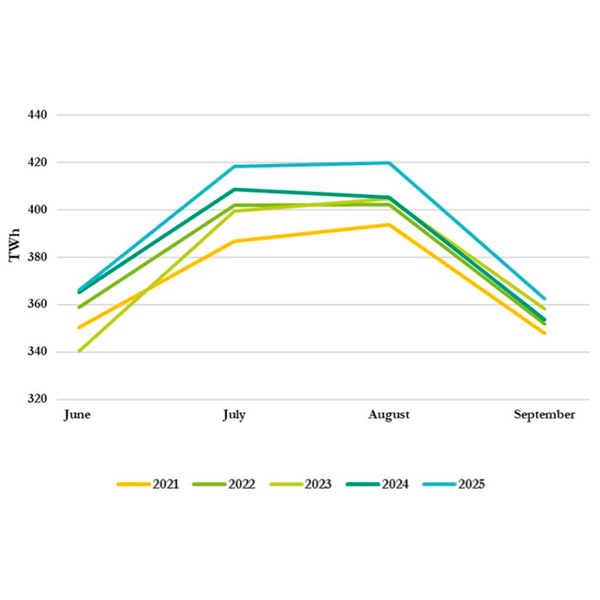
FERC's summer assessment shows rising demand and prompted Chair Mark Christie to discuss recent developments in PJM.
Texas Reliability Entity CEO Jim Albright sees similarities between the issues facing the U.S. and European grid and hopes to learn from the recent Iberian Peninsula outage.
With winter storms, load sheds and tight operating conditions, 2025 has turned out to be “quite a challenging year” for SPP.
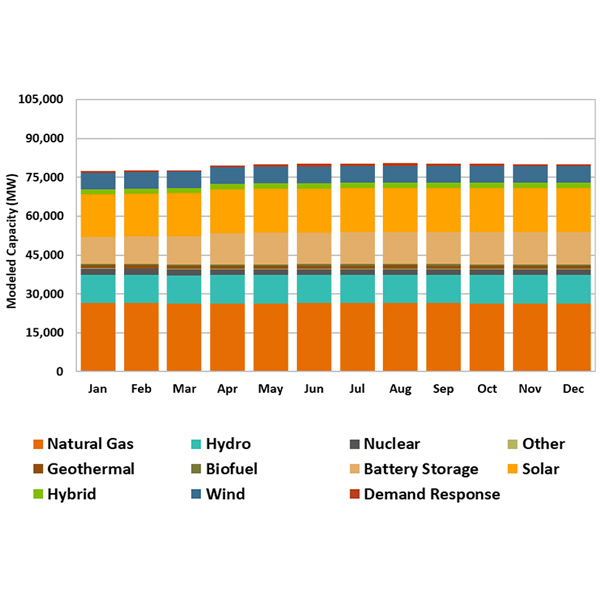
California expects to meet its peak demand this summer under most weather conditions due to thousands of megawatts of new energy resources — almost all battery storage.
Efforts by U.S. House committees to mark up the “One, Big Beautiful Bill” that includes most of President Donald Trump’s legislative goals could so complicate energy tax credit provisions as to make those instruments difficult to use at all.
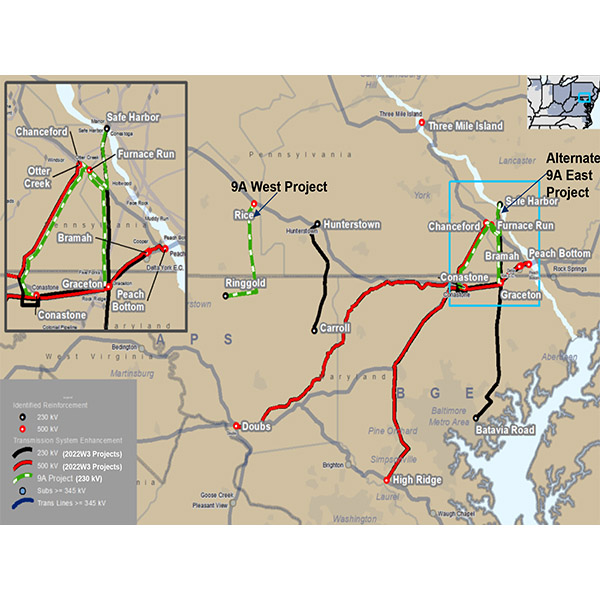
PJM presented additional details about the projects selected for expedited interconnection studies through the Reliability Resource Initiative to the Planning Committee.
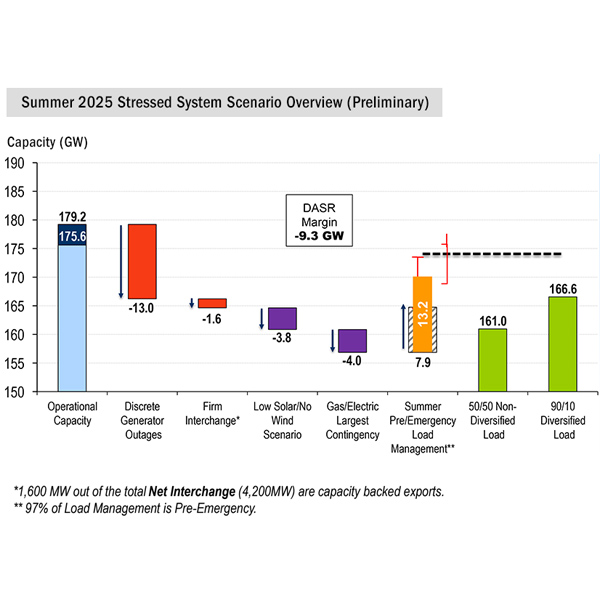
The preliminary results of PJM’s look ahead at the capacity available for this summer and the expected peak loads suggest that about 5.4 GW of demand response could be needed to maintain the 3.5-GW real-time primary reserve requirement.
Want more? Advanced Search