Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
NYISO CEO Rich Dewey presented the ISO's annual Power Trends report, noting that shrinking reliability margins could force fossil fuel plant retirement delays.
Last September, California residents helped the state avert rolling blackouts by acting on an emergency text. What does that mean for RA planning?
The PJM Markets and Reliability Committee voted to reject manual changes on the synchronized reserve requirement.
Testifying before the Senate, NERC's CEO warned that increased reliance on weather-dependent renewables will likely lead to more frequent grid disruptions.
FERC on Tuesday accepted a MISO tariff filing, promising to annually update an unforced capacity-to-intermediate seasonal accredited capacity ratio.
Texas regulators rejected SWEPCO's application to build renewable generation resources at the site of a coal plant that ceased operations in March.
Western regulators heard from a power panel of CEOs on maintaining grid reliability in the face of fires, storms, extreme heat and supply chain disruptions.
MISO will evaluate through the end of the year how it can measure and encourage six generating attributes that it says are necessary to its system operations.
MISO said that a sloped demand curve applied to its recent seasonal auction would have boosted summer clearing prices as much as sixfold.
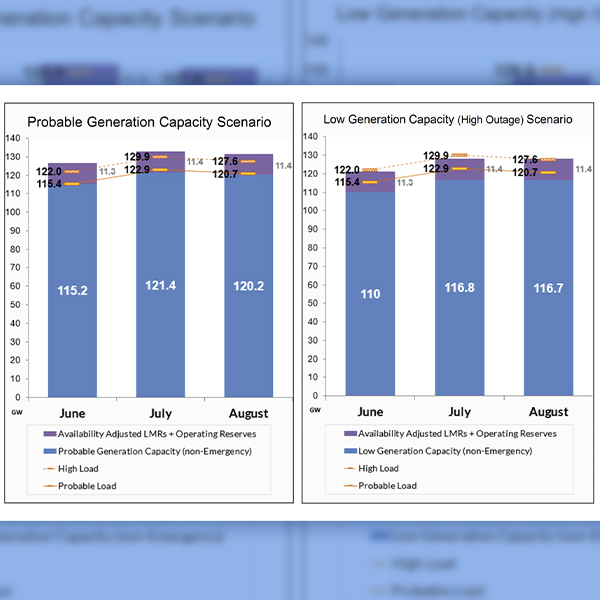
MISO this week said it will likely operate with almost no firm generating capacity to spare to manage typical summertime peaks.
Want more? Advanced Search