Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
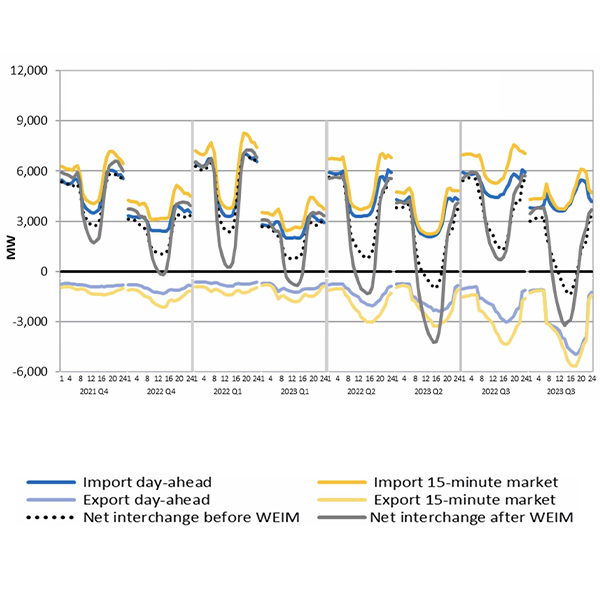
CAISO's Department of Market Monitoring explained that self-scheduled exports to support stressful conditions led to the declaration of emergency alerts in July.
Hoping for a mild winter is not a sustainable plan for reliability, FERC Chairman Willie Phillips said at a NEPOOL Participants Committee meeting.
PJM reviewed changes in preparation for the winter season and urged generators to participate in Systems Operations Subcommittee calls ahead of storms.
After four rounds of voting, the New York State Reliability Council Executive Committee approved a 22% IRM for 2024/25, up from 20% for the previous year.
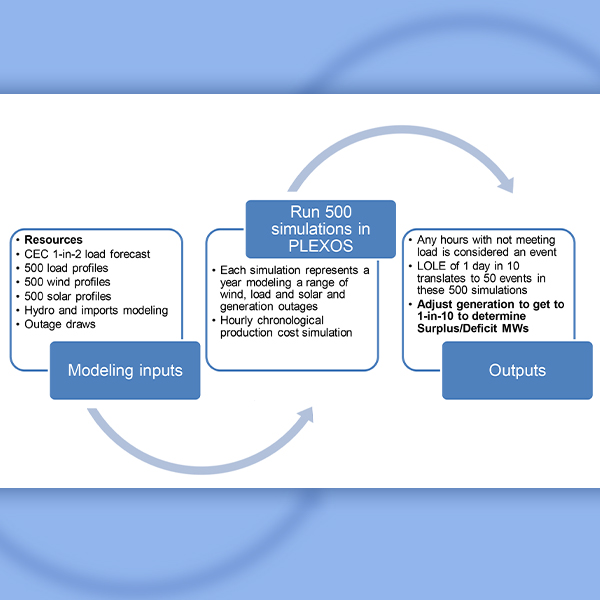
CAISO staff and stakeholders again dove into the details of the ISO’s resource adequacy construct, including potentially creating year-ahead requirements and refining the existing capacity procurement mechanism.
SPP REAL Team members conducted a “therapy session” in forming a consensus position around its schedule and priorities for 2024.
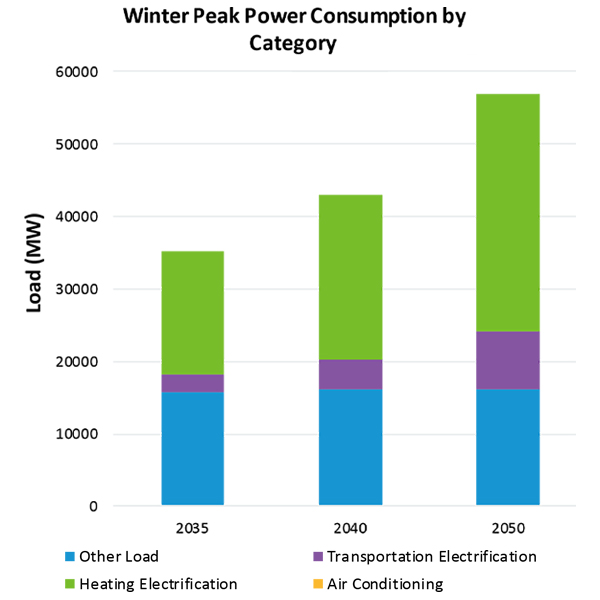
ISO-NE forecasts peak demand of 20,269 MW under average weather conditions, and a 21,032-MW peak under below-average temperatures.
NYISO’s new 10-year reliability plan finds no “actionable reliability needs,” but warns of narrowing reliability margins.
The PJM Markets and Reliability Committee endorsed new generation winterization requirements, followed by the Members Committee approving three changes to the stakeholder process.
MISO CEO John Bear and PJM CEO Manu Asthana expressed concerns about gas-fired resources retiring prematurely at NARUC's Annual Meeting in California.
Want more? Advanced Search