Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
FERC Commissioner Mark Christie brought his message of the need for grid reliability to the Gulf Coast Power Association's MISO-SPP Forum, saying the U.S. is "heading for a very dark place."
Two Tennessee congressmen have introduced a bill to force TVA to make its integrated resource planning process more transparent.
Nevada regulators approved NV Energy’s plan to convert its last coal-fired power plant to natural gas, while also allowing the company to move forward with a $1.5 billion, 400-MW solar-plus-storage project.
Utility executives told state regulators that natural gas and nuclear power will be part of the electric mix for decades as the industry decarbonizes.
MISO is determined to file with FERC by the end of March to introduce a probabilistic capacity accreditation that’s controversial among its stakeholders.
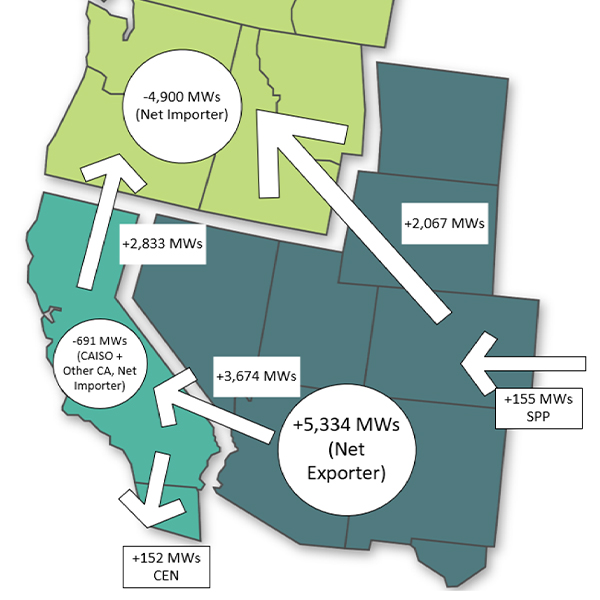
Imports from the Southwest and Rockies helped the Northwest survive January’s cold, showing the region’s reliability is at a “tipping point,” WPP said.
Ohio and Pennsylvania lawmakers met in Columbus for a hearing on the future reliability of the PJM grid, quizzing RTO and industry insiders on the role states can have in maintaining resource adequacy.
FERC approved PJM's proposal to rework several areas of its capacity market centered around aligning how resources’ capacity contributions match up to system risk analysis.
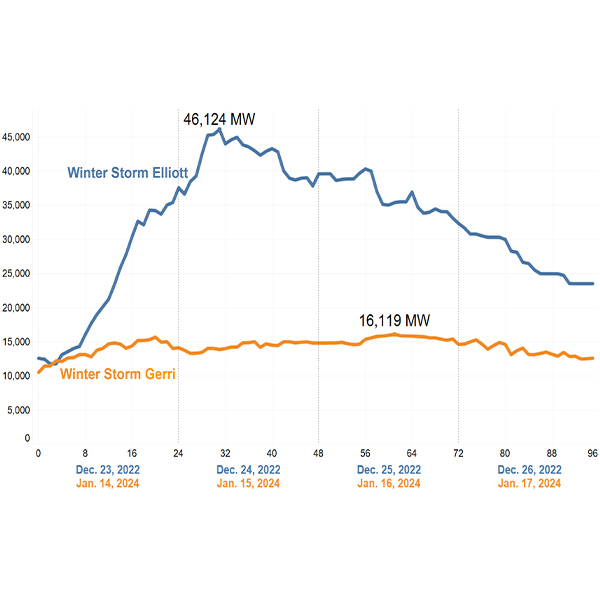
PJM said the grid maintained reliability through nearly a week of harsh winter conditions during the winter storm that blanketed much of the nation in mid-January.
CAISO staff and stakeholders are looking to re-evaluate the RA Availability Incentive Mechanism and explore whether it should be replaced with a new program using an unforced capacity construct to ensure sufficient RA capacity.
Want more? Advanced Search