Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
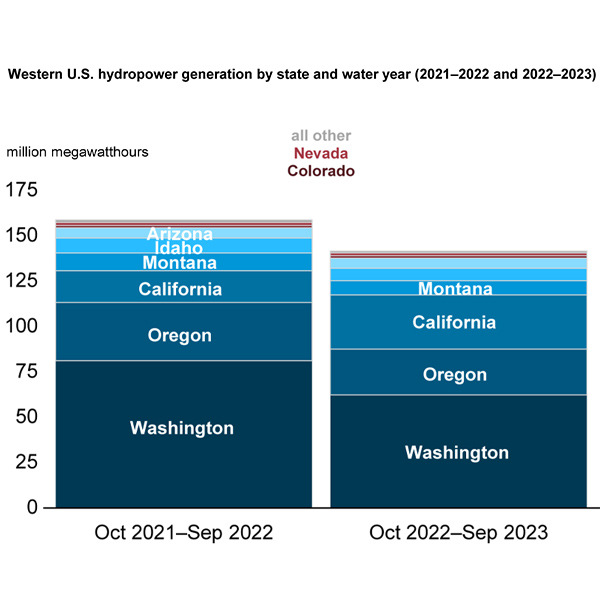
Despite record winter precipitation in California, hydroelectric generation in the Western U.S. fell to a 22-year low in the 2022/23 water year, largely due to drought conditions in Washington and Oregon.
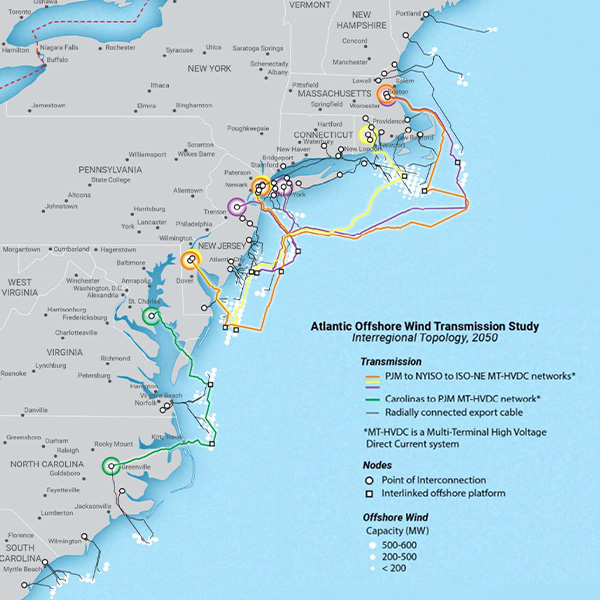
Offshore wind is projected to be a key part of East Coast states’ decarbonization and DOE called its two-year study the most thorough analysis to date.
Texas regulators have adopted a new rule establishing the Texas Energy Fund In-ERCOT Generation Loan Program, a $5 billion fund designed to bring new dispatchable power projects to the state.
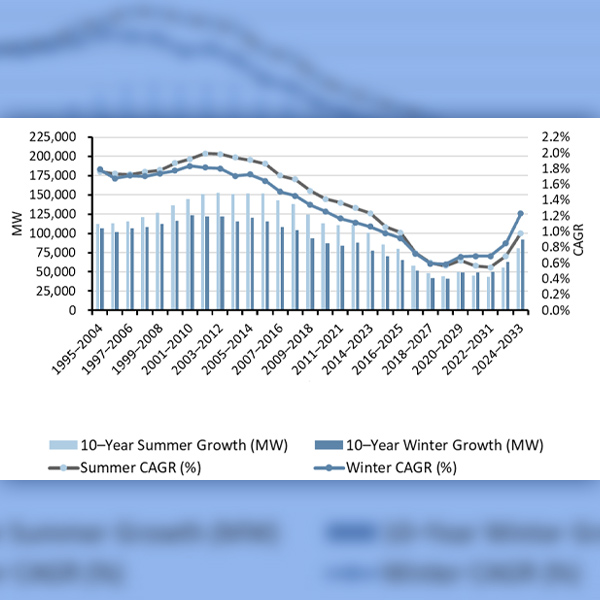
2023 began with a mild winter, setting the pace for a relatively quiet year in which natural gas and wholesale electricity prices dropped and the U.S. added a net 26 GW in generation capacity.
Multiple MISO members appeared skeptical at their quarterly meetings that the RTO is destined to face capacity shortfalls before the turn of the decade.
The Washington Post’s warning that “America is running out of power” lacks context and distracts us from the real work at hand, says columnist Steve Huntoon.
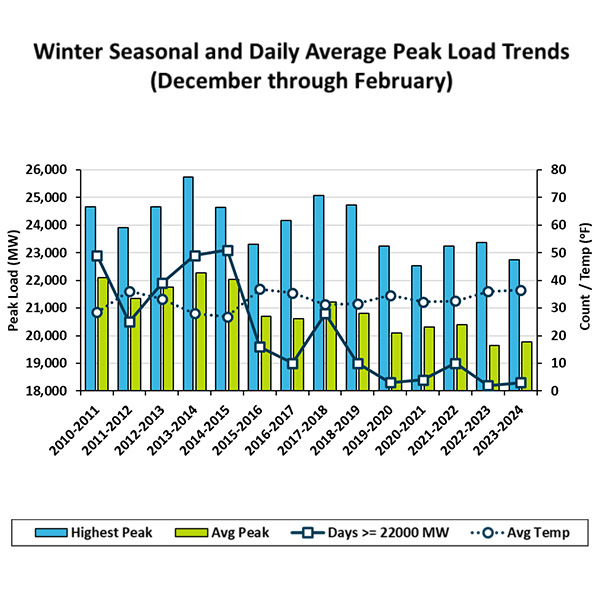
The Operating Committee was briefed on one of NYISO’s most humdrum winters, characterized by high temperatures, low gas prices and below-average loads.
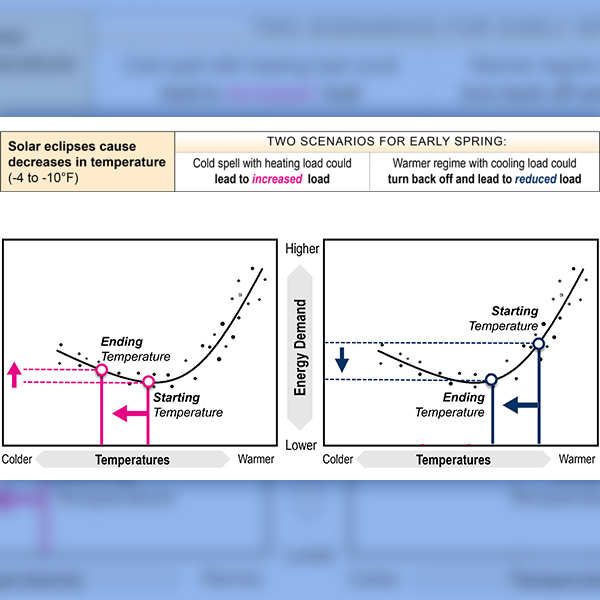
PJM's Operating Committee discussed low reserve response during a spin event in February and the possible impact April's solar eclipse could have on generation and load.
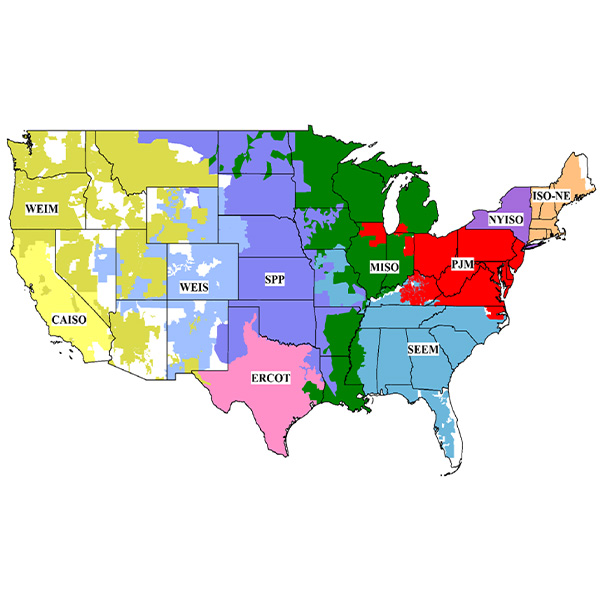
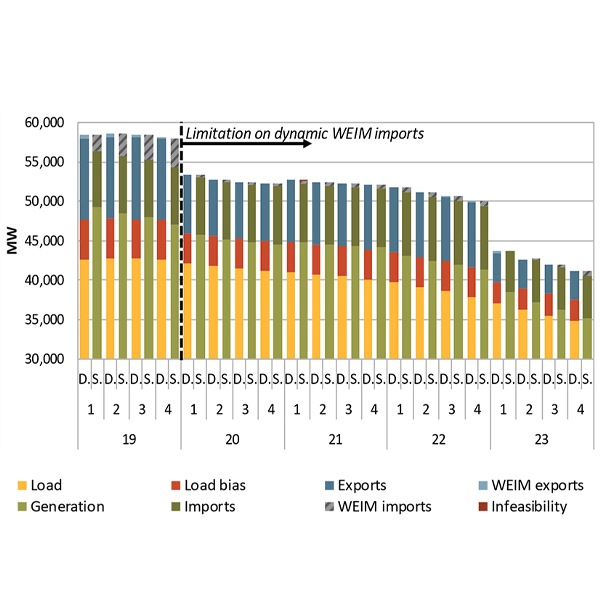
CAISO's Department of Market Monitoring found that limits on WEIM imports last year led to increased transmission congestion in the ISO's markets.
FERC Commissioner Mark Christie brought his message of the need for grid reliability to the Gulf Coast Power Association's MISO-SPP Forum, saying the U.S. is "heading for a very dark place."
Want more? Advanced Search