Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
NYISO sad it expects enough capacity to serve peak load this summer under normal conditions, but hotter-than-expected weather could lead it to resort to emergency procedures.
The Texas Reliability Entity says its latest regional assessment indicates weatherization activities since the disastrous February 2021 winter storm have paid off.
There’s no going back on waning capacity in MISO, panelists agreed at a gathering of state regulators, though predictions of escalating load growth have some skeptical.
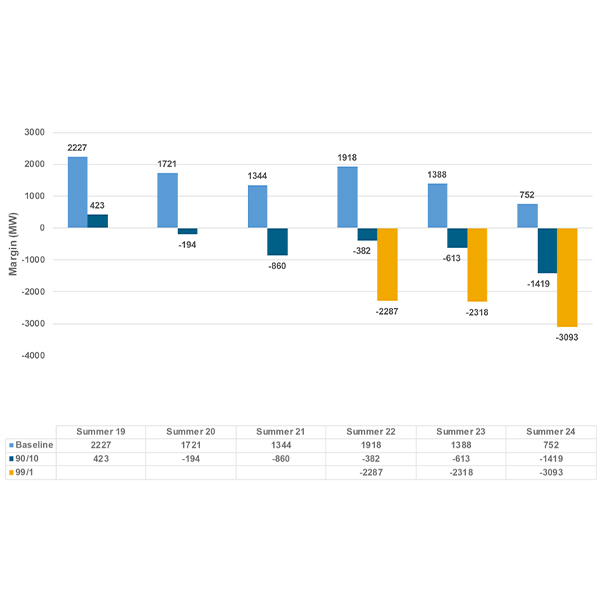
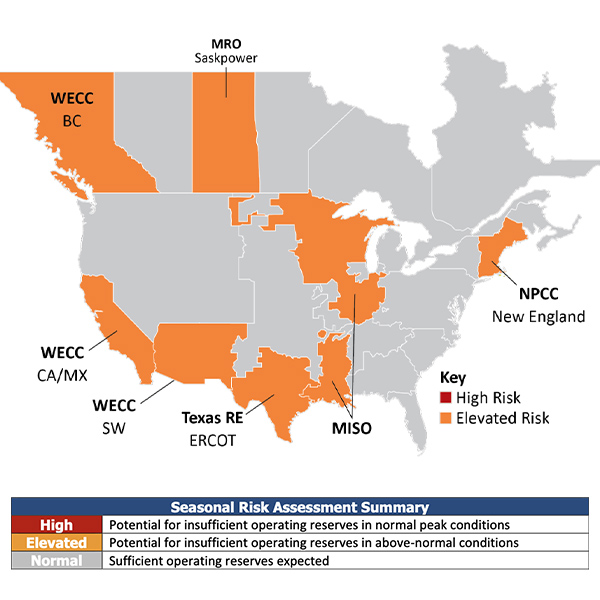
NERC’s 2024 Summer Reliability Assessment found that every region has met its reserve margin targets but that many areas would face difficult operations in lengthy, widespread heat waves.
ISO-NE outlined its current thinking on a potential Regional Energy Shortfall Threshold at the NEPOOL Reliability Committee.
Three years after a deadly winter storm nearly imploded the ERCOT grid, stakeholders in the Texas market are working on a reliability standard that may be stricter than industry norms.
SPP CEO Barbara Sugg warned the RTO’s board and stakeholders that the grid operator faces new and stronger headwinds, even as it met its corporate goals’ first-quarter milestones.
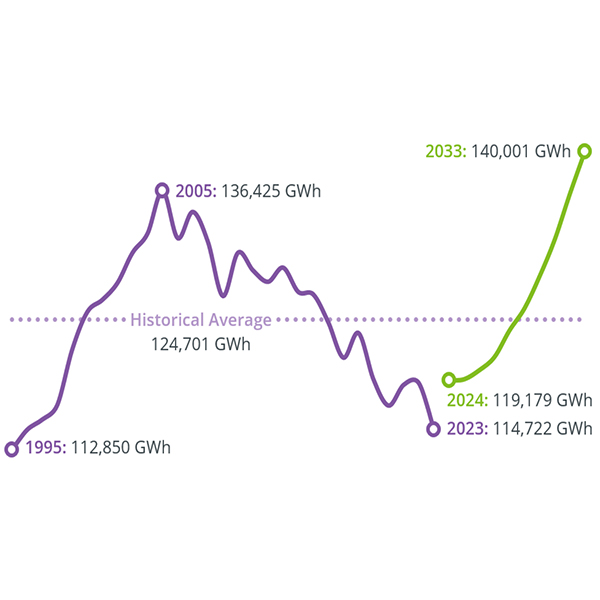
ISO-NE is predicting that New England’s peak load will increase by about 10%, and electricity consumption by 17%, by 2033, according to its 2024 Capacity, Energy, Loads and Transmission report.
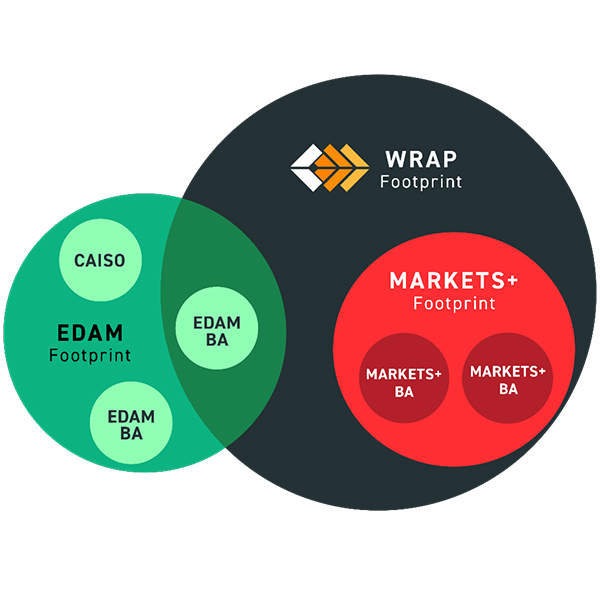
Members of a key WRAP stakeholder group have expressed support for the recent move by participants to delay the program’s “binding” penalty phase by one year, to summer 2027.
Ameren executives have reassured shareholders that Missouri’s capacity shortfall beginning this summer is no cause for panic.
Want more? Advanced Search