Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
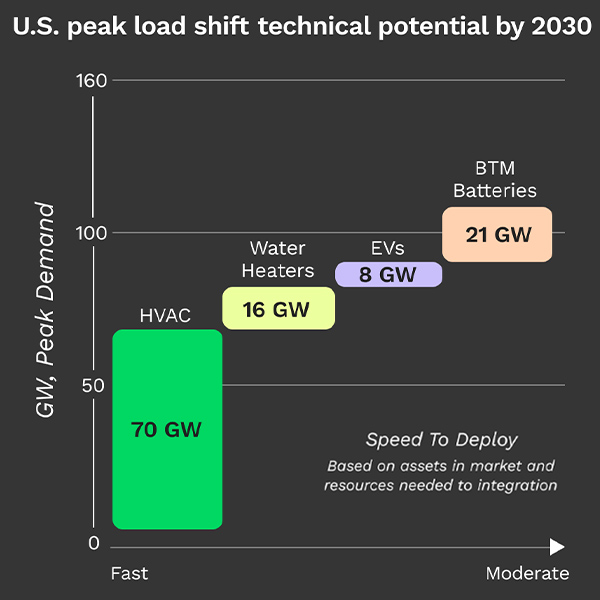
Home energy management company Renew Home has released a position paper arguing that VPPs can quickly be stood up to help meet growing demand.
SPP directors and regulators have approved the grid operator’s first winter planning reserve margin, endorsing a base PRM that is 3 percentage points higher than many of its utilities wanted.
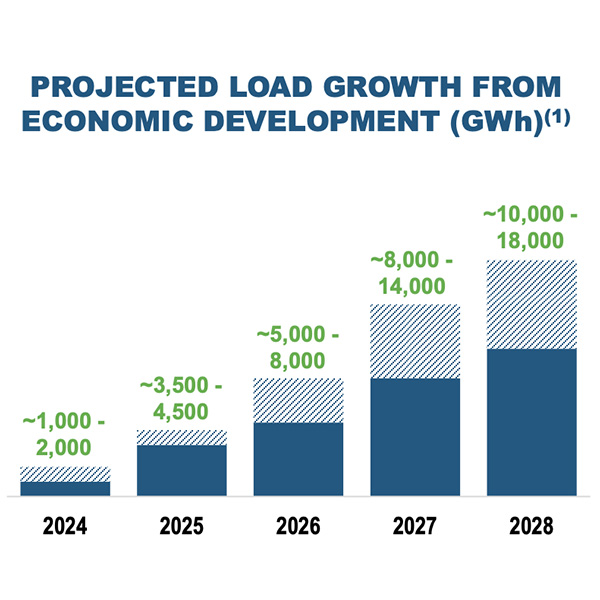
Five years ago, load growth from transportation electrification was a major issue for policymakers, according to speakers at a webinar. Now the focus has shifted to data centers.
Duke Energy executives highlighted how the return to load growth is impacting its utilities during its second-quarter earnings call with analysts.
PPL reported GAAP earnings of $190 million for the second quarter and executives focused on changing market dynamics in PJM during a teleconference with analysts.
The Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee voted 15-4 to advance the Energy Permitting Reform Act of 2024 to the floor.
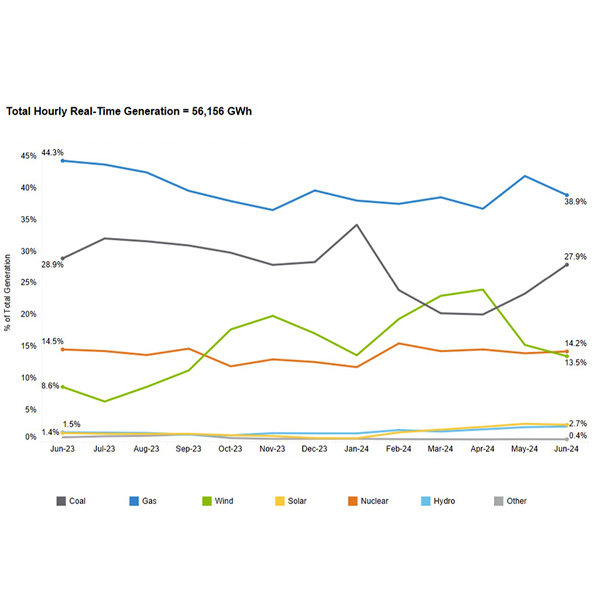
June brought a 2-GW lower peak than anticipated and unchanged real-time and fuel prices from last year, MISO said in a monthly operations report.
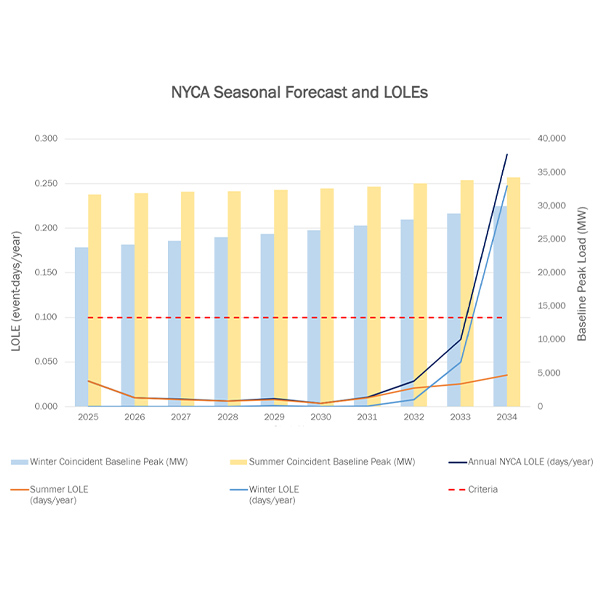
New York will be short 1 GW of resources by 2034, driven by increased demand, large load growth and lack of natural gas, according to the preliminary results of NYISO's biennial Reliability Needs Assessment.
FERC approved NYISO’s proposed tariff revisions to more accurately accredit natural gas resources’ capacity, but the commission delayed their implementation until 2026.
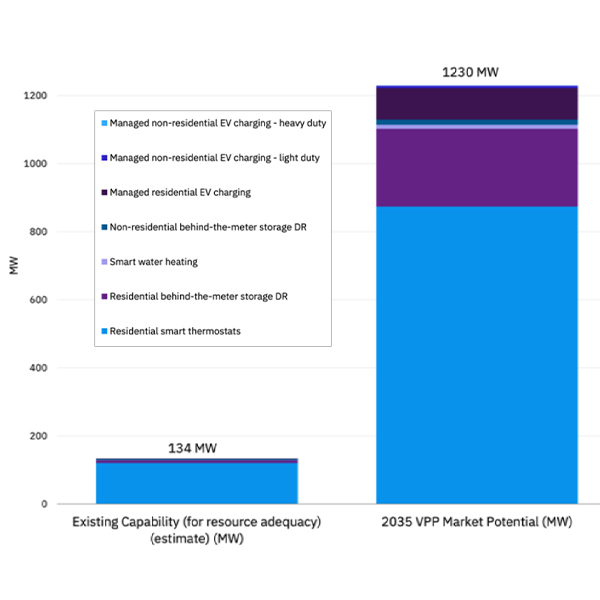
NV Energy's virtual power plant market potential could grow from an estimated 134 MW this year to 1,230 MW in 2035, according to a new analysis.
Want more? Advanced Search