New York
Vermont signed onto the multistate Northeast Clean Hydrogen Hub, one of the many joint state proposals competing for federal funding from the H2Hub program.
New York Gov. Kathy Hochul released a legislative framework for the cap-and-invest program she is proposing to help the state meet its GHG-reduction goals.
The price of New York ZECs is set to fall 14% for the next two years after the agency that administratively sets the price issued its biennial price adjustment.
New York Gov. Kathy Hochul is proposing a significant expansion of the role of the New York Power Authority, the nation’s largest state-owned utility.
Long-duration energy storage company Zinc8 Energy Solutions plans to build its first factory in Kingston, N.Y., the company and Gov. Kathy Hochul announced.
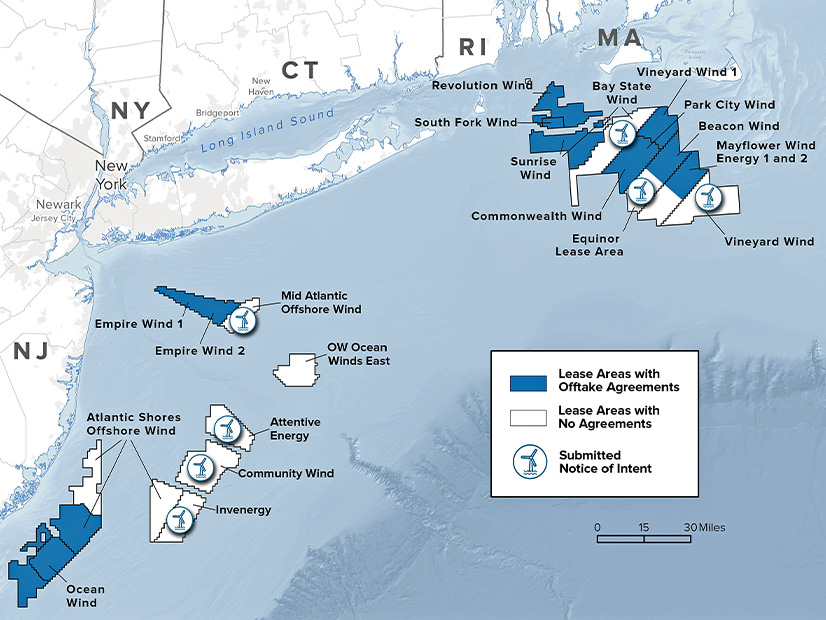
New York said its latest offshore wind solicitation drew more than 100 proposals from six developers for eight new projects — a record level of response.
FERC conditionally accepted NYPA's proposal to revise its formula rate template in response to its need to bring on large amounts of clean generation.
NYSERDA did not release details on the submissions for New York state’s third offshore wind solicitation, but least some of the would-be developers are known.
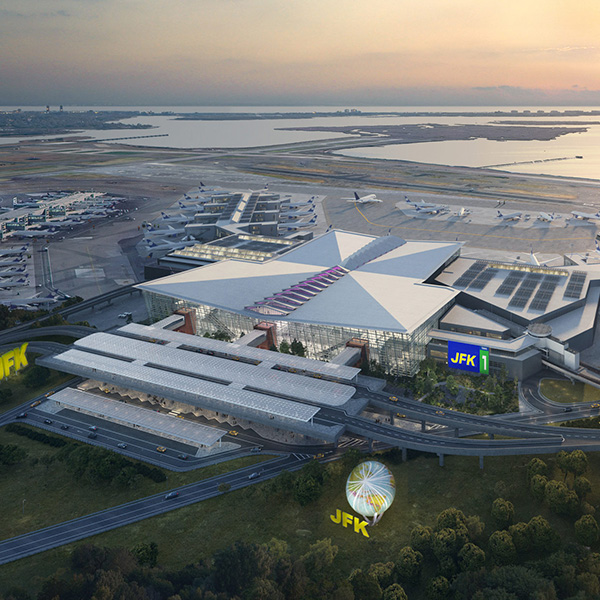
New York’s JFK Airport is planning an 11.3-MW microgrid powered by solar and fuel cells to cut emissions and continue operations during power outages.
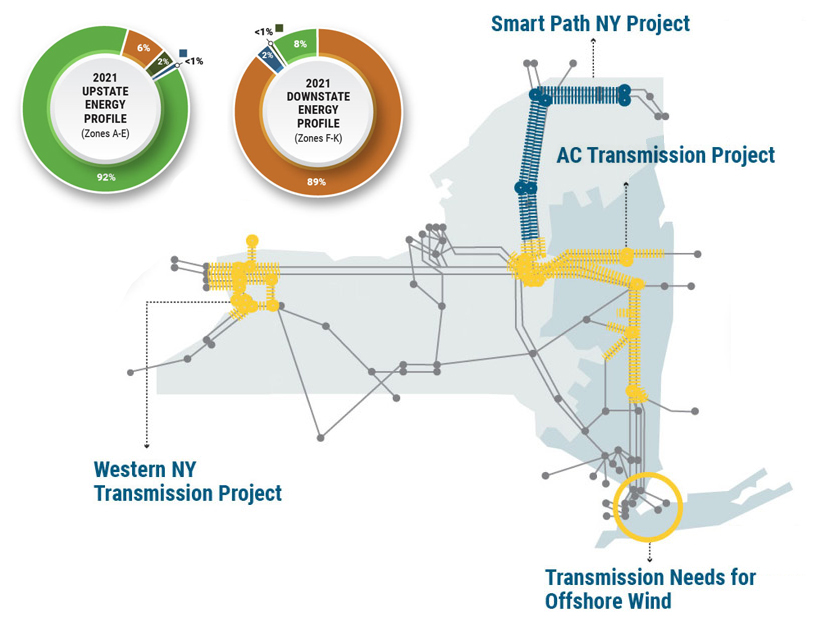
NYISO rebuked NextEra Energy for attempting to lobby the grid operator to award it transmission projects to connect offshore wind projects to Long Island.
Want more? Advanced Search