Public Policy
Environmental RegulationsReliabilityState & RegionalAlabamaAlaskaArizonaArkansasCaliforniaColoradoConnecticutDelawareDistrict of ColumbiaFloridaGeorgiaHawaiiIdahoIllinoisIndianaIowaKansasKentuckyLouisianaMaineManitobaMarylandMassachusettsMichiganMinnesotaMississippiMissouriMontanaNebraskaNevadaNew HampshireNew JerseyNew MexicoNew YorkNorth CarolinaNorth DakotaOhioOklahomaOregonPennsylvaniaRhode IslandRTO-IndianaSouth CarolinaSouth DakotaTennesseeTexasUtahVermontVirginiaWashingtonWest VirginiaWisconsinWyoming
Recent developments made speakers at the annual New York Energy Summit optimistic that the state's permitting process will be getting faster.
FERC dealt with a rehearing request in Order 1920-B, largely rebutting arguments from transmission owners that the rule's requirement to file state cost allocation agreements impinges on their rights.
State officials speaking at the New York Energy Summit acknowledged the uncertainty facing everyone in the room but said it has not changed the state's clean-energy vision.
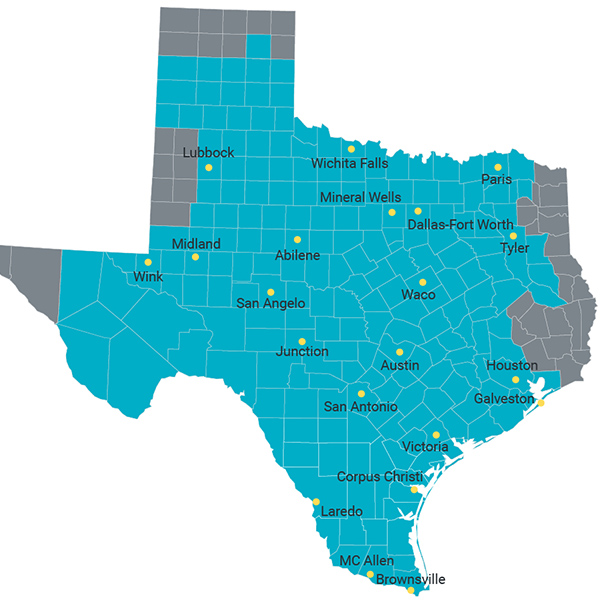
ERCOT, Oncor and the Texas PUC asked FERC to deny a petition from Puerto Rican company Pluvia to bring the territory under the commission’s jurisdiction.
NYISO continues to find a reliability need for New York City this summer and two peaker plants in the city should be allowed to continue operations into 2027 if necessary, according to sensitivity results for the first-quarter Short Term Assessment of Reliability.
President Donald Trump signed a series of executive orders that seek to keep existing coal-fired power plants running, ease regulations and permitting for coal mining, and remove “unlawful and burdensome” state laws that impede the industry.
MISO’s proposal to use a temporary “fast lane” in its interconnection queue to speed up necessary resource additions would give utility-owned generation preferential treatment, according to protesters’ comments filed with FERC.
As the Department of Energy explores using federal land for data centers powered by nuclear power, experts say public-private risk-sharing will be crucial to make nuclear a viable option.
New Jersey lawmakers pushed back on the state’s all-electricity, clean-energy strategy at a heated committee hearing, urging an all-the-above approach as PJM faced criticism for failing to foresee a dramatic hike in demand.
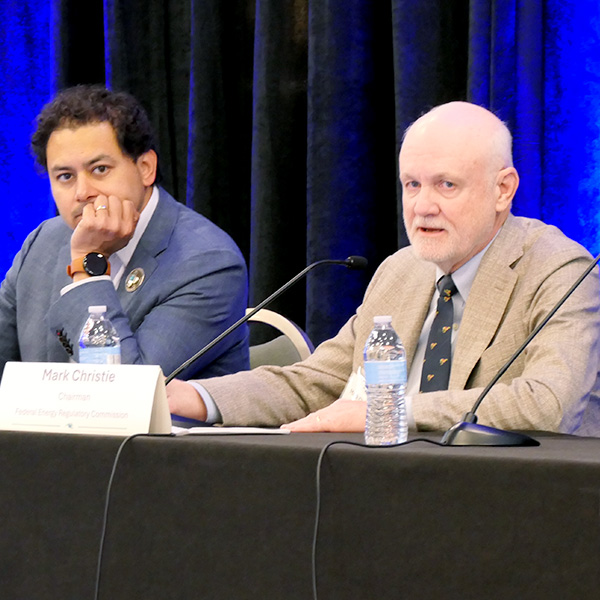
FERC Chair Mark Christie and Commissioner Judy Chang downplayed the current political environment’s impact on the agency, saying the commission’s role is to follow the law and ensure the fairness of procedures.
Want more? Advanced Search