ISO-NE
ISO-NE Consumer Liaison GroupISO-NE Planning Advisory CommitteeNEPOOL Markets CommitteeNEPOOL Participants CommitteeNEPOOL Reliability CommitteeNEPOOL Transmission Committee
ISO New England Inc. is a regional transmission organization that oversees the operation of the electricity transmission system, coordinates wholesale electricity markets, and manages power system planning for the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, Massachusetts, Vermont, New Hampshire, and most of Maine.
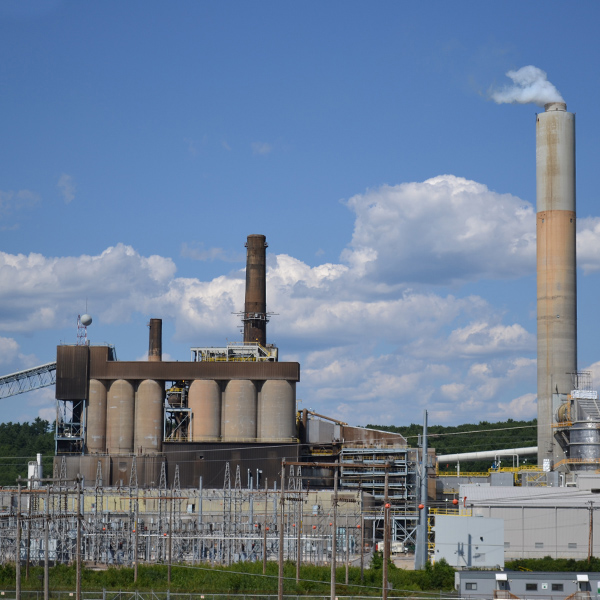
Granite Shore Power has reached an agreement with EPA, the Sierra Club, and the Conservation Law Foundation to retire New England's last coal plant by 2028.
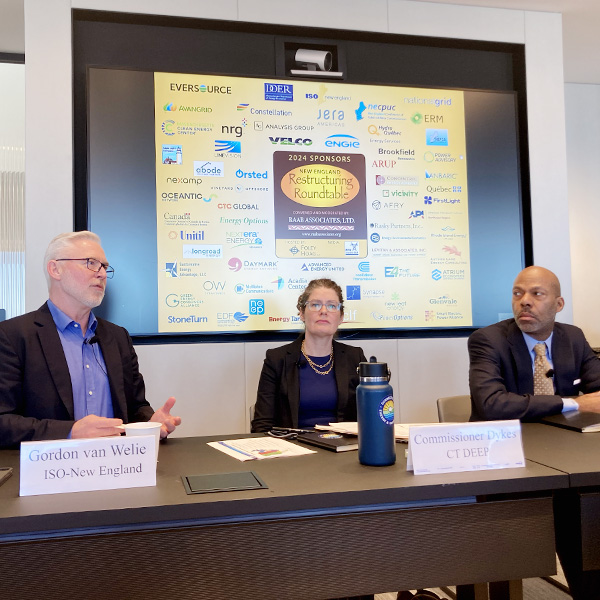
As intermittent renewables proliferate in New England, the region must do a better job incentivizing reliable, dispatchable resources that can support the grid as it decarbonizes, speakers at a Raab Associates roundtable said.
An event by Advanced Energy United drew connections between the infrastructure needs of the clean energy transition and Boston’s Big Dig highway project.
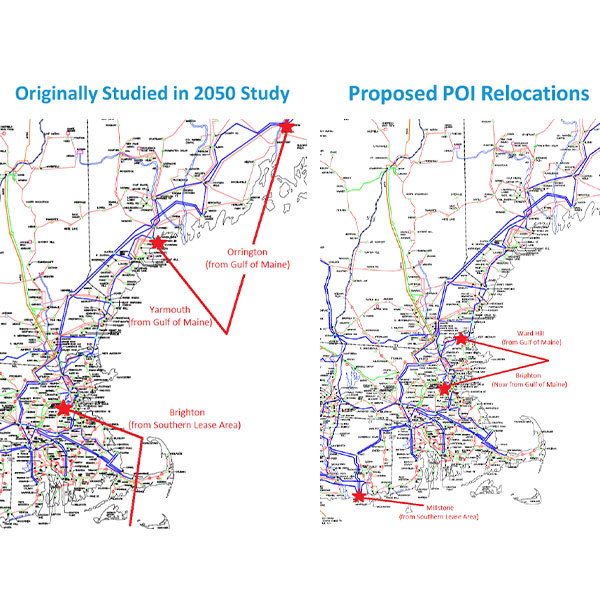
ISO-NE is planning to study the effects of shifting two offshore wind points of interconnection from Maine to Massachusetts and conduct a preliminary analysis of offshore wind interconnection points across the region.
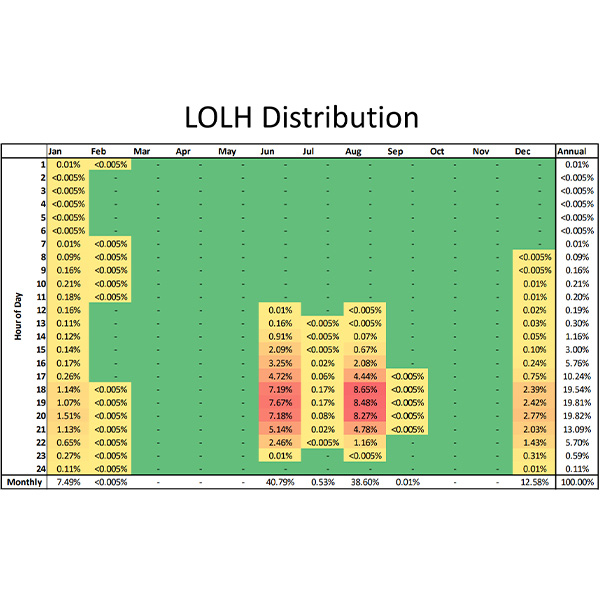
ISO-NE presented the NEPOOL Markets Committee with additional results of the impact analysis for the RTO’s resource capacity accreditation project, which looked at how changes to the resource mix would affect the seasonal distribution of shortfall risks.
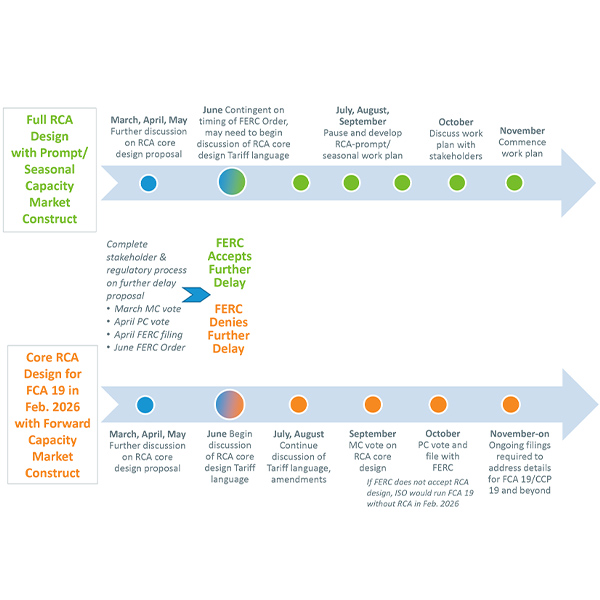
The NEPOOL Markets Committee approved an additional two-year delay of ISO-NE’s Forward Capacity Auction 19 to develop and implement a new seasonal capacity auction.
Transmission limits remain a major barrier to scaling up wind and solar energy to meet state decarbonization goals, speakers at the NECA’s Renewable Energy Conference said.
The NEPOOL Participants Committee unanimously approved ISO-NE’s package of tariff revisions to comply with FERC Order 2023.
Speakers at the ISO-NE Consumer Liaison Group meeting stressed the importance of proactive efforts to unlock the potential of demand response and peak shifting.
Avangrid reported a year-over-year decrease in income but said a timely pause in its offshore wind projects saved it from write-offs that could have run into the billions.
Want more? Advanced Search