FERC & Federal
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.
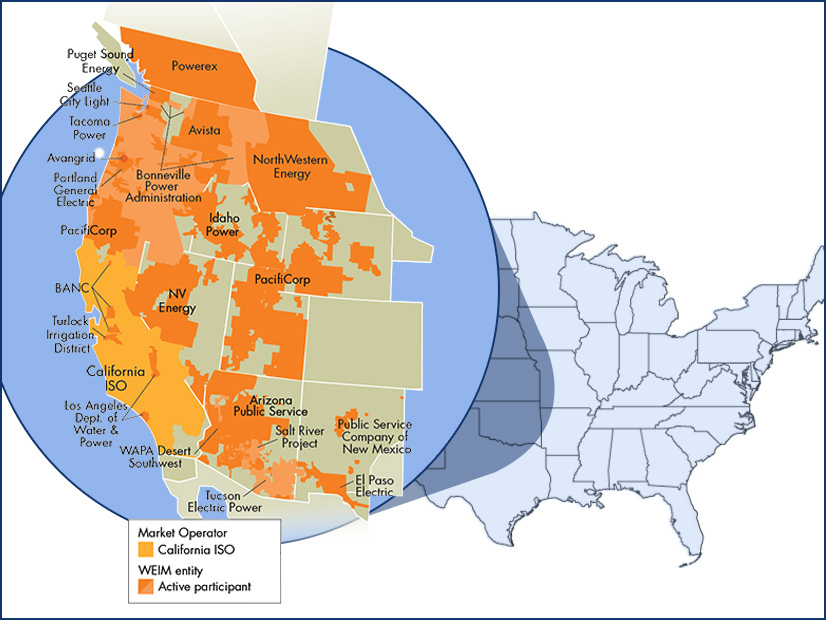
Three new entities joined CAISO's Western Energy Imbalance Market, including El Paso Electric, which expanded the market into Texas for the first time.
Nautilus Power asked FERC to dismiss penalties over the December 2022 storm, saying PJM failed to provide sufficient notice for their units to purchase gas.
U.S. OSW developers must follow Europe’s example and build out meshed HVDC systems, experts told the International Partnering Forum.
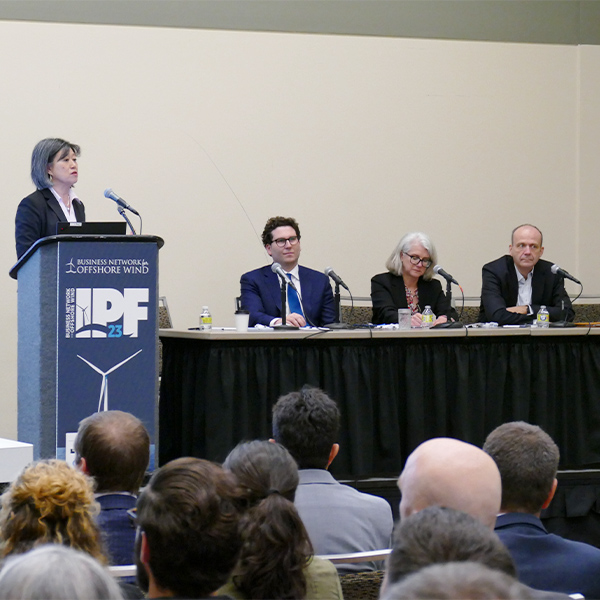
With major projects being completed this year, OSW is poised to become a major source of electricity and good jobs, panelists at a BNOW conference said.
The PJM Board of Managers on Monday announced it will seek a delay in the 2025/26 Base Residual Auction scheduled for this June, as well as future auctions.
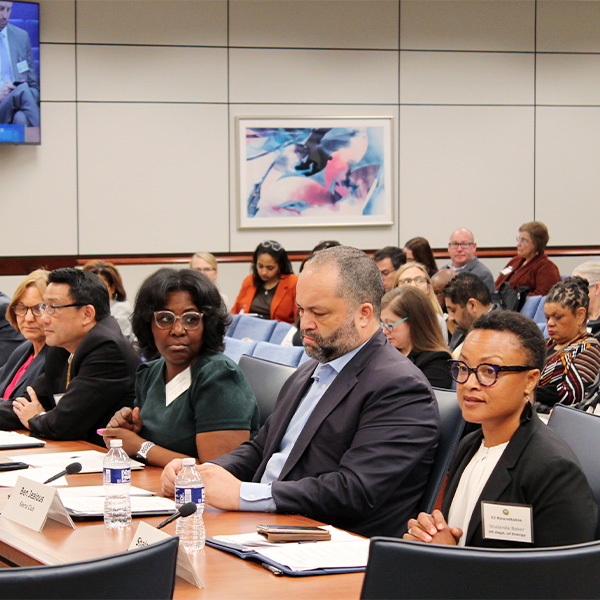
FERC received passionate testimony from panelists at its roundtable on incorporating environmental justice and equity into its infrastructure permitting.
DOE's proposal to update efficiency standards for distribution transformers would make supply shortages of the key grid equipment worse, industry argued.
State regulators and others urged FERC to increase oversight of “local” transmission projects while TOs insisted existing cost controls are sufficient.
The U.S. must change permitting processes to deploy federal infrastructure money and ensure CO2 reductions needed to avoid the worst climate change impacts.

David Maiolo, CC BY-SA-3.0, via Wikimedia
House Republicans are moving the first energy permitting bill through Congress, but it lacks any provisions around electric transmission.
Want more? Advanced Search