Energy Storage
With the end of Massachusetts’ legislative session looming, lawmakers are on the clock to reach an agreement on a major climate bill centered around clean energy permitting and siting reform.
The California Public Utilities Commission is proposing to authorize procurement of emerging clean energy technologies with a combined nameplate capacity of up to 10.6 GW.
Questions from energy reporters at a USEA briefing on emerging cleantech shifted the focus to what will happen to U.S. energy policy if Donald Trump is re-elected president.
Rhode Island Gov. Dan McKee signed into law a bill that sets a target of 90 MW of energy storage installed by Dec. 31, 2026; 195 MW by the end of 2028; and 600 MW by the end of 2033.
The New York PSC approved a roadmap to reach the state's goal of 6 GW of energy storage by 2030.
After 23 years at Southern California Edison and eight as a consultant at ICF International, Gene Rodrigues was four months into retirement in 2022 when he got a call from the Department of Energy’s Office of Electricity.
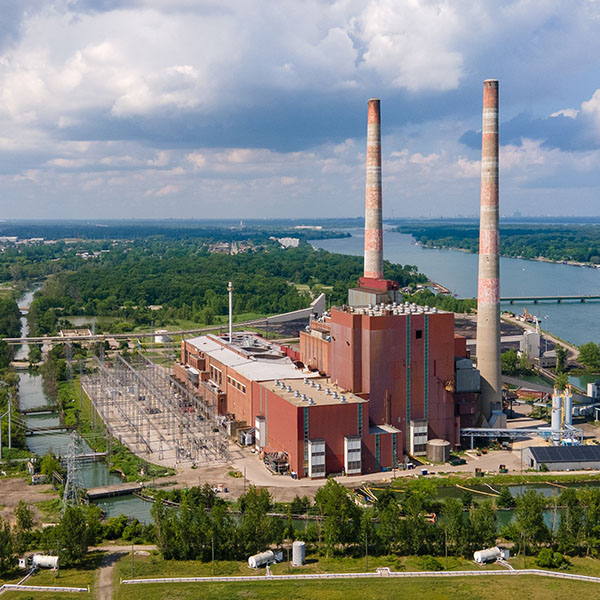
With a capacity of 220 MW and 880 MWh, the Trenton Channel Energy Center is expected to be the largest standalone battery storage site in the Great Lakes region when completed in 2026.
The use of distributed energy resources can reduce grid costs, delay system upgrades, authors contend.
A developer has committed to replacing a fossil-fired peaker plant with a lithium-ion battery system that will, for a while, be New York City's largest.
Battery storage remains largely reliant on state programs and subsidies to be viable in Massachusetts but could increasingly stand on its own as renewable energy proliferates, a panel of energy storage experts said.
Want more? Advanced Search