Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.
FERC in November 2024 granted a 48-month preliminary permit to York Energy Storage LLC for an 858-MW facility along the Susquehanna River near Lancaster and York that could produce 1.5 million MWh per year.
The D.C. Circuit rejected an appeal of FERC's approval of two pipelines in Louisiana tied to a planned LNG site.
The D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals has reversed its vacatur of FERC's approvals of two LNG export facilities in Texas.
While the majority of IRA tax credits and incentives have gone to develop clean energy projects in Republican districts and states, House leadership leans heavily toward fossil fuel-producing states,
To build a reliable, affordable and clean electric power system, the U.S. energy industry and customers will need to shift their thinking about what a reliable system looks like, according to a study from nonprofit think tank Energy Innovation Policy & Technology.
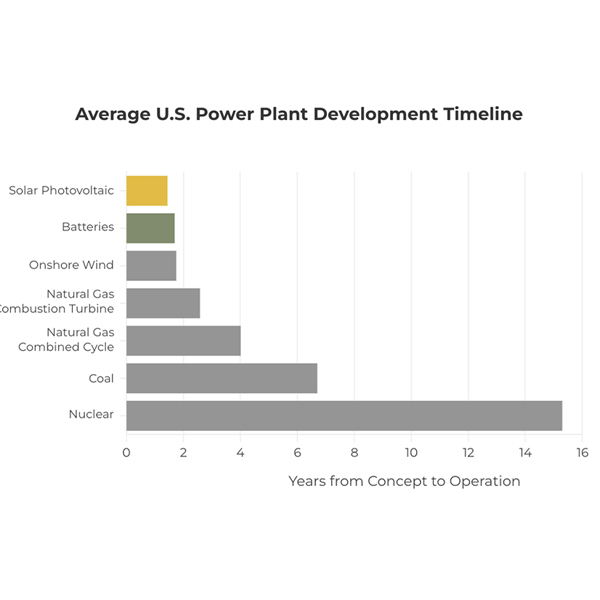
The U.S. electric power industry faces unprecedented challenges from the size, pace and impacts of demand growth and should look to new approaches for possible solutions, according to speakers at NASEO’s Energy Policy Outlook Conference.
A North American trade war was delayed for a month at least as Canada and Mexico struck deals with President Trump that delayed potential tariffs for a month.
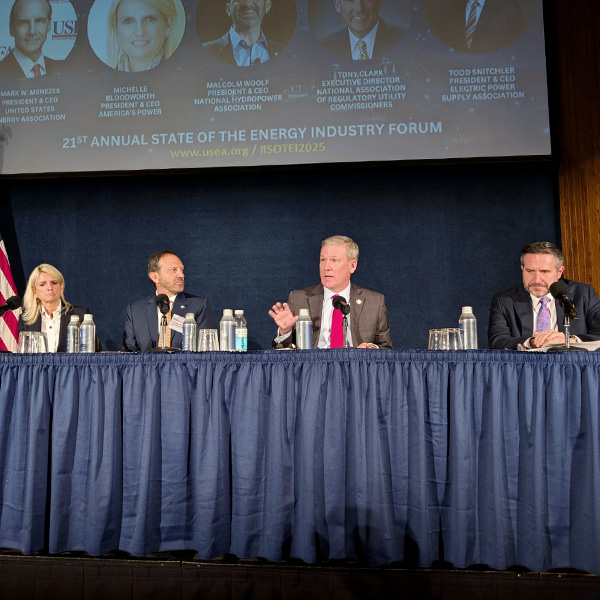
Participants at the United States Energy Association’s 2025 State of the Energy Industry Forum discussed topics such as demand growth, nuclear fusion and energy efficiency.
FERC issued an order terminating its proceeding on the consideration of greenhouse gas emissions in natural gas infrastructure project reviews.
The D.C. Circuit found the commission appropriately approved a new pipeline in Indiana meant to serve new natural gas generation that the state approved.
Want more? Advanced Search