FERC & Federal
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.

David Maiolo, CC BY-SA-3.0, via Wikimedia
Congressional Republicans stepped up attacks on the Biden Administration's energy policies this week, attempting to leverage the debt ceiling to force change.

Matthew T. Rader, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
FERC said last week that “by operation of law” it would not reconsider its approval of one of NERC’s new cold weather reliability standards.
FERC took the last step in fulfilling its obligation to encourage voluntary investments in cybersecurity by electric utilities, as directed by Congress in 2021.
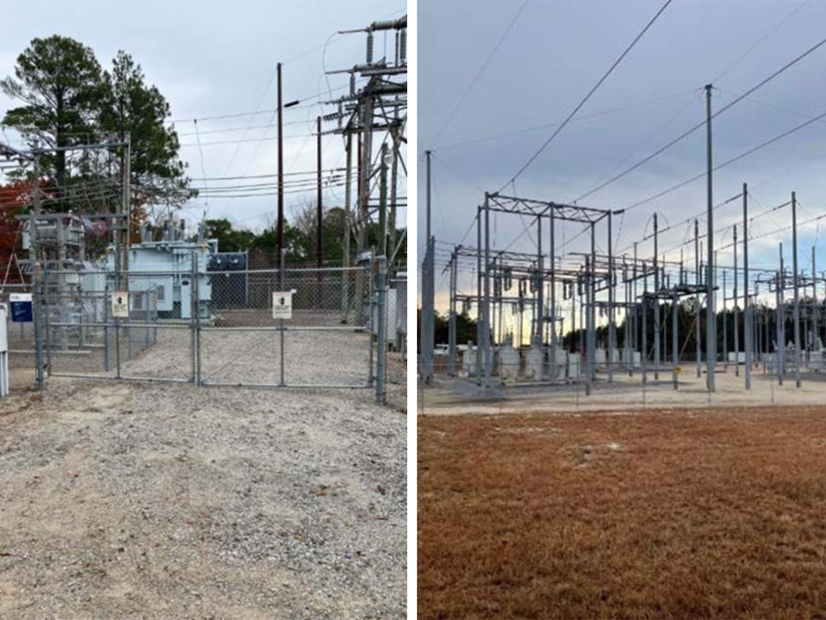
NERC will consider changes to its reliability standard for physical security in response to the threat of violence against grid assets.

Travis Goodspeed, CC BY-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Biden's cybersecurity strategy may backfire by alienating tech companies that should be the government's allies, commentator Shahid Mahdi says.

Farragutful, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
PJM will pay $140,000 to ReliabilityFirst as part of a settlement for violations of NERC reliability standards at several facilities, including 2 nuclear sites.
FERC must look beyond reliability standards to boost electric industry winter readiness, says R Street Institute's Michael Giberson.
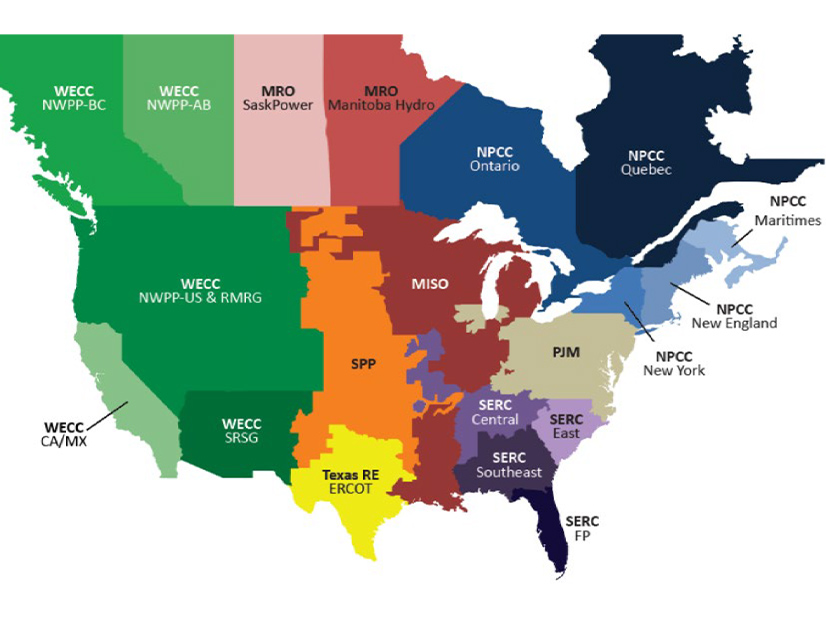
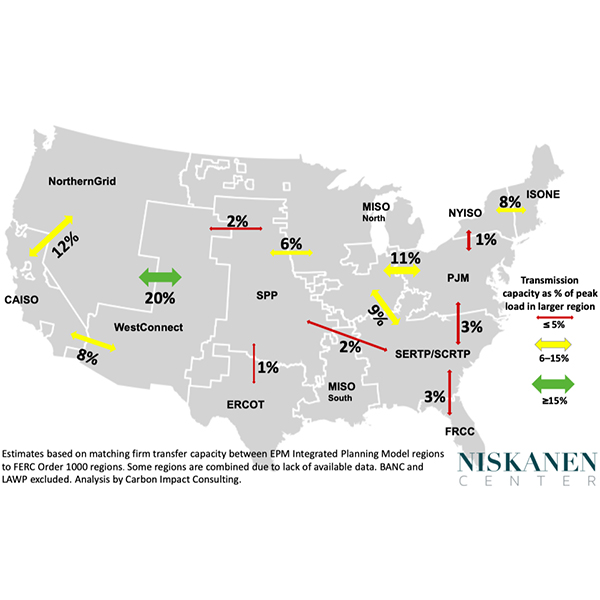
FERC must act to strengthen interregional transmission ties to improve reliability, says former Arkansas PSC Chair Ted Thomas.
While none of the incidents affected reliability, evidence of attackers’ efforts to sabotage the grid “highlights the continued need for vigilance,” NERC said.
Senators discussed new bills that would give FERC authority over gas pipeline cybersecurity and change how DOE handles cyber threats.
Want more? Advanced Search