FERC & Federal
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.
FERC approved NERC reliability standards affecting transmission system planning performance and communications cybersecurity.
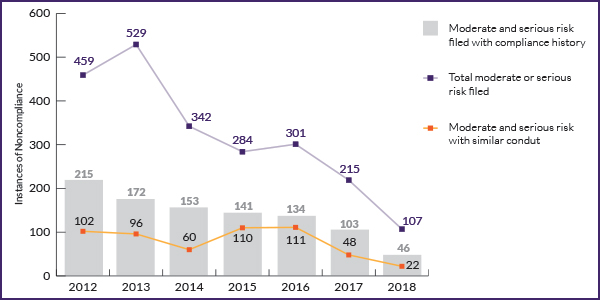
FERC recertified NERC as the ERO for another five years while ordering the organization to audit its regional entities and improve oversight of the E-ISAC.
Hackers who once focused on oil and gas producers have been increasingly targeting the electric grid, according to a new report by ICS security firm Dragos.
Although fears of an imminent U.S. military conflict with Iran have eased, cybersecurity experts cautioned the country remains an increasing cyber threat.
FERC urged the FCC to conduct additional testing to ensure automated frequency coordination will protect utilities’ use of the 6 GHz spectrum band.
FERC allowed Duke to treat its Cybersecurity Informational Technology-Operational Technology Program as a single project for calculating allowance for funds.
Comments on a proposal to ensure generators are prepared for cold-weather events revealed widespread skepticism over the value of pursuing new standards.
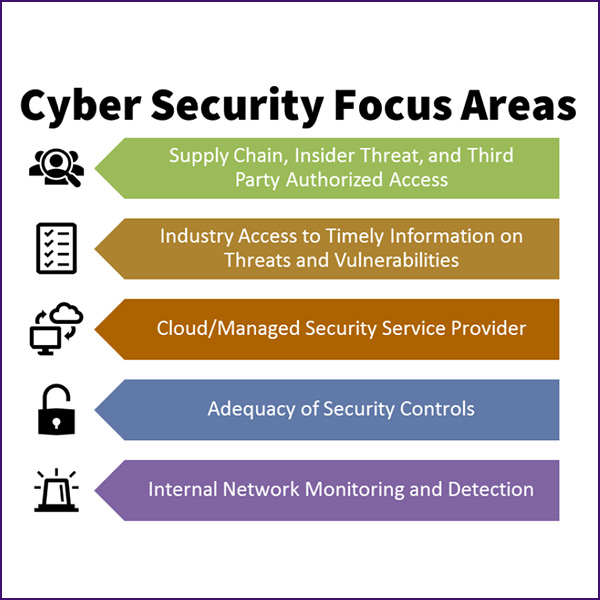
FERC is rethinking its cybersecurity strategy by reorganizing two departments and directing its efforts at five “focus areas.”
Limits of grid exercises and simulation tools, and the need to prepare for a cyberattack were themes at the National Academies’ conference on grid security.
NERC opened a ballot on a proposal requiring entities that fail to meet performance requirements for “supplemental” GMD events to develop corrective plans.
Want more? Advanced Search