Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
SERC said in its Long-Term Reliability Assessment that continued active collaboration with registered entities and other stakeholders is needed to address growing reliability concerns.
The power industry is facing an increasingly delicate balancing act as policies drive some generators to retirement, while major new loads are popping up and making planning more difficult.
Ohio and Pennsylvania lawmakers met in Columbus for a hearing on the future reliability of the PJM grid, quizzing RTO and industry insiders on the role states can have in maintaining resource adequacy.
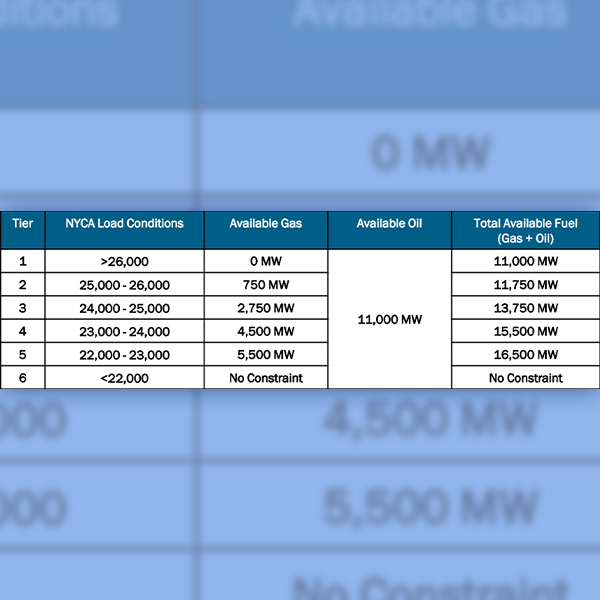
NYISO briefed the committee on an upcoming white paper to propose updates to the ISO’s resource adequacy modeling.
NERC issued a warning to the electric industry to expect serious challenges amid expected severe winter weather.
Both EPA and FERC received comments on how reliability can be maintained under the former’s power plant rule that requires fossil fuel-fired units to curtail their emissions.
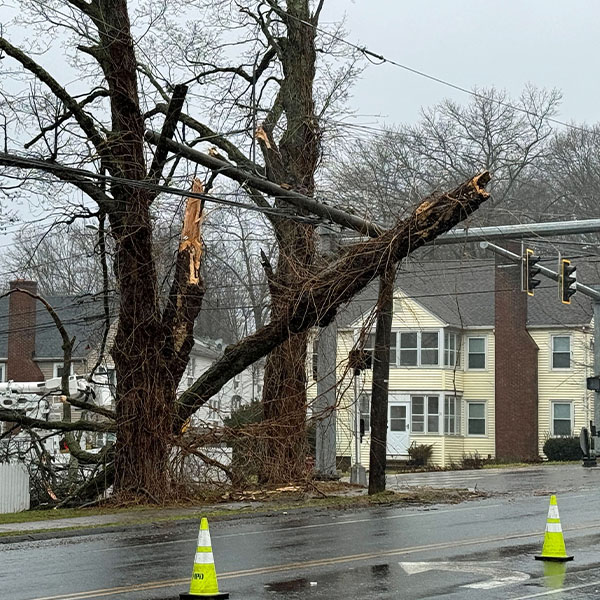
Hundreds of thousands of electric utility customers lost electric power Dec. 18 as wind and rain hit the Northeast.
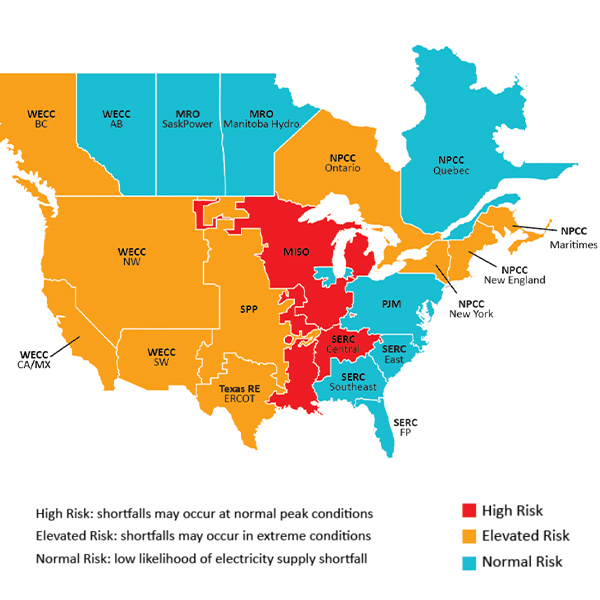
NERC's Long-Term Reliability Assessment sees some risk for reliability issues in most of the country as the industry has to deal with faster demand growth and shifting supplies of generation.
As the transition to clean energy contributes to the risk of energy shortfalls, electric industry stakeholders say keeping the grid operating reliably will require new ways of thinking.
Speakers on an ACORE webinar warned that the national security risks of electricity outages at military bases is unappreciated.
Want more? Advanced Search