Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
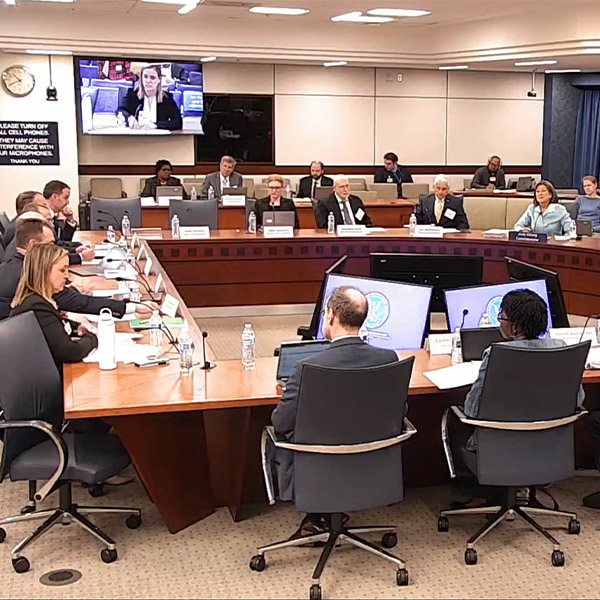
Grid stakeholders joined commissioners in Washington, D.C., for FERC's annual Reliability Technical Conference.
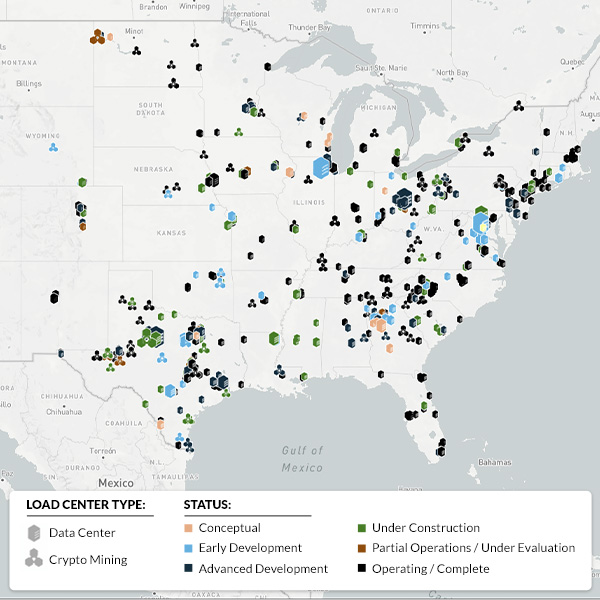
Pairing power-hungry data centers with clean energy resources is sparking mixed feelings among regulators, who say the grid already is straining with increased electrification and connecting new energy sources.
FERC's annual Reliability Technical Conference will feature discussions on resource adequacy and other pressing grid reliability concerns.
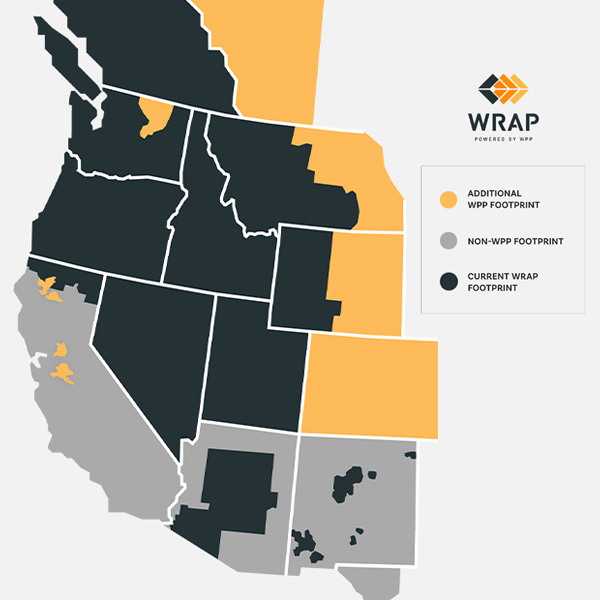
The Western Resource Adequacy Program’s key stakeholder body approved a plan that would postpone the start of its penalty phase by one year, to summer 2027.
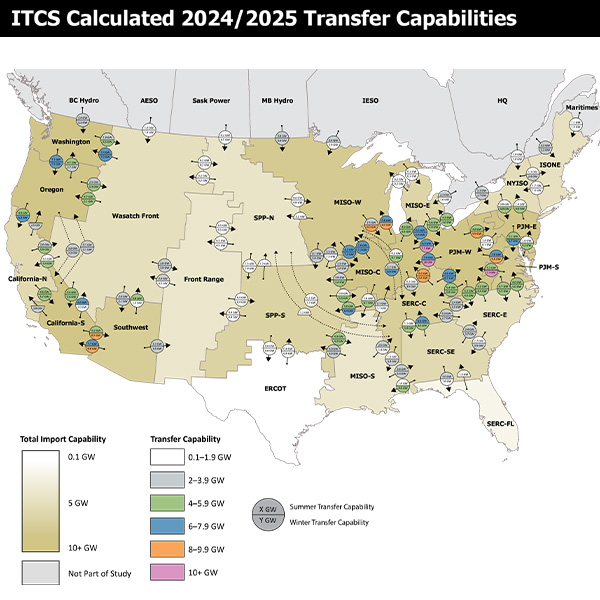
NERC released the first installment of the federally mandated ITCS in draft form this week.
Five years ago, load growth from transportation electrification was a major issue for policymakers, according to speakers at a webinar. Now the focus has shifted to data centers.
A new report from NERC and the National Academy of Engineering explored the shortcomings of traditional resource adequacy metrics and alternatives under development.
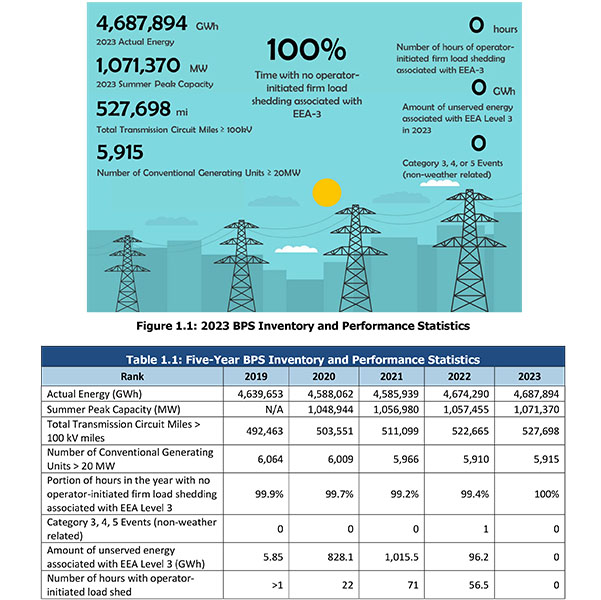
NERC's 2024 State of Reliability Report noted resilience in the face of extreme weather last year, along with growing rates of generator forced outages.
NPCC said all subregions should have adequate supply to meet demand this summer despite recent generation retirements.
Data center expansion is a major part of the power industry’s return to demand growth around the country, and the United States Energy Association hosted a webinar with industry leaders on how the sector’s growth will play out.
Want more? Advanced Search