NERC & Committees
The North American Electric Reliability Corp., a not-for-profit authority, regulates reliability and security standards for the bulk power system in the continental U.S., Canada, and the northern portion of Baja California, Mexico. NERC is subject to oversight by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission and governmental authorities in Canada

Farragutful, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
FERC approved NERC's June spreadsheet notice of penalty, including settlements over reliability standard violations submitted by SERC and MRO.

foam, CC BY-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
FERC approved NERC's removal of language from CIP-014 requiring compliance evidence to be stored on site.
NERC's Standards Committee approved four standard authorization requests at its meeting on Wednesday.
FERC approved two NOPRs on Thursday aimed at improving utilities' planning for the long-term impacts of climate change to the bulk power system.
More than 200,000 AEP customers in Ohio lost power after storms damaged multiple transmission lines and forced load sheds on at least three 138-kV lines.
NERC added two new reference documents to its website in an effort to consolidate its work on inverter-based resources and distributed energy resources.
The DOE's message is clear: interconnecting solar, wind and other clean energy projects to the grid must be made simpler, faster and fairer.
NERC's Reliability and Security Technical Committee agreed to endorse two new standards projects at its meeting this week, while rejecting another.
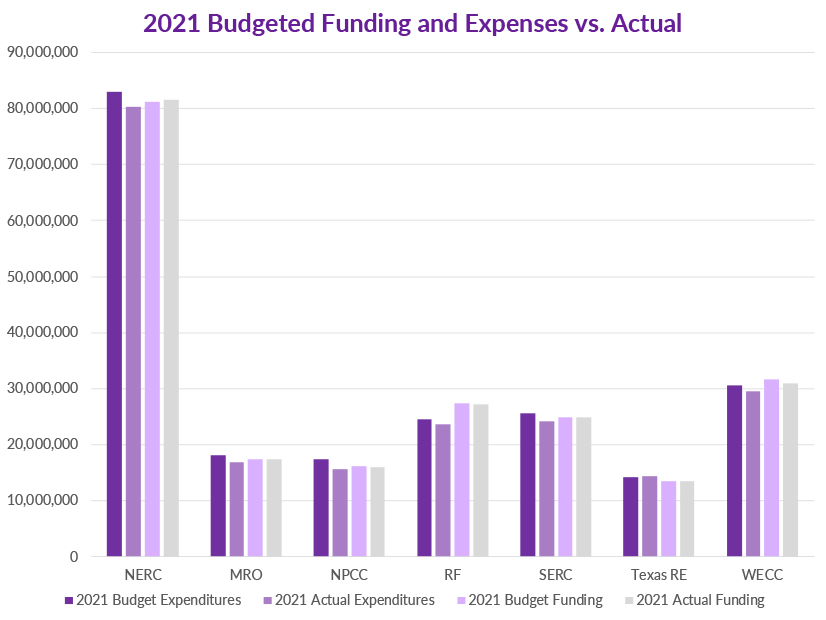
NERC and the regional entities said the ongoing shutdown of business travel and remote work postures from COVID-19 helped fuel budget savings in 2021.
Finance officers across the ERO Enterprise said that inflation and cybersecurity investments will be major drivers of budget increases in 2023.
Want more? Advanced Search